OM301
解剖学 Anatomy
解剖学是研究生物体内部结构的科学,包括生物体的形态、组织结构、器官之间的关系。解剖学通常通过观察和研究生物体的内部和外部结构来揭示生物体的组织构造和器官功能。
Anatomy is the science that studies the internal structure of an organism, including its shape, tissue structure, and the relationship between organs. Anatomy usually reveals the tissue structure and organ functions of an organism by observing and studying its internal and external structures.
解剖学又有很多分支,系统解剖学是解剖学的一个分支,主要研究人体各个系统的结构、组成和功能。这些系统包括运动系统(肌肉、骨骼),循环系统(心脏、血管)、消化系统(胃、肠道)、呼吸系统(肺部、气管)、泌尿系统(肾脏、膀胱)、内分泌系统(腺体、激素)、神经系统(大脑、脊髓)等。
Anatomy has many branches. Systemic anatomy is a branch of anatomy that mainly studies the structure, composition and function of various systems of the human body. These systems include the motor system (muscles, bones), the circulatory system (heart, blood vessels), the digestive system (stomach, intestines), the respiratory system (lungs, trachea), the urinary system (kidneys, bladder), and the endocrine system (glands). , hormones), nervous system (brain, spinal cord), etc.
时间表schedule
概况Overview
骨骼skeleton
肌肉muscle
关节joint
感觉器官sense organs
Class | Date | Topic |
1 | Sep. 9 | Skeleton-1 |
2 | Sep. 16 | Skeleton-2 |
3 | Sep. 23 | Muscle |
4 | Sep. 30 | Holiday |
5 | Oct. 7 | Joints |
6 | Oct. 14 | Ear & Eyes |
7 | Oct. 21 | Midterm (90mins) Review |
8 | Oct. 28 | endocrine system |
9 | Nov.4 | nervous system |
10 | Nov. 11 | Holiday |
11 | Nov. 18 | respiratory system |
12 | Nov. 25 | cardiovascular system |
13 | Dec. 2 | digestive system |
14 | Dec. 9 | urinary system |
15 | Dec. 16 | Final exam (90mins) Review |
基本解剖学术语 Anatomical Terms
1.解剖学位置 Anatomical position
人体直立,两眼向正前方平视,两上肢自然下垂,手掌向前,两足并立,足尖向前。
The human body is upright, with eyes looking straight ahead, both upper limbs drooping naturally, palms facing forward, feet standing side by side, toes pointed forward.
2.方位术语 Direction terms
上 下: Superior - Inferior
前 后: Anterior- Posterior (腹侧 « 背侧)
内侧 « 外侧:Medial « Lateral
浅 « 深:Superficial « Deep
近侧 « 远侧:Proximal « Distal
1.上(颅侧)与下(尾侧) 近颅者为上,近足者为下。
The upper (cranial side) and lower (caudal side) ones closer to the head are upper, and those closer to the feet are lower.
2.前(腹侧)与后(背侧) 近腹者为前(腹侧),近背面者为后(背侧)。
Front (ventral) and back (dorsal) The one close to the abdomen is the front (ventral), and the one close to the back is the back (dorsal).
3.内侧与外侧 近正中面者为内侧,远离正中面者为外侧。
Medial and lateral sides: The one close to the midline is called the medial side, and the one far away from the midline is called the lateral side.
4.内与外 近内腔者为内,远内腔者为外。
Inside and outside: The one closest to the inner cavity is called the inner cavity, and the one farther away from the inner cavity is called the outer cavity.
5.浅与深 近皮肤者为浅,离皮肤远而近人体内部中心者为深。
Shallow and deep: those close to the skin are shallow, and those far away from the skin and close to the center of the human body are deep.
6.近侧与远侧 在四肢,距肢体根部近者为近侧,离肢体根部远者为远侧。
Proximal and distal In the limbs, the one close to the root of the limb is the proximal side, and the one farthest from the root of the limb is the distal side.
3. 断面术语 Plane terms
矢状面: Sagittal planes:
将人体分成左、右两部分的纵切面 若将人体分成相等的左、右两半的断面,称正中矢状面。
The longitudinal section that divides the human body into left and right parts. If the human body is divided into two equal halves, it is called the median sagittal plane.
冠状面: Coronal planes
将人体分成前、后两部分的断面。
A cross section that divides the human body into front and back parts.
水平面: Transverse planes
与上述两个平面相垂直,将人体分成上、下两部分的断面。
Transverse planes that is perpendicular to the above two planes and divides the human body into upper and lower parts.
1.骨的分类 Classification of Bones
位置 Position
中轴骨: 颅骨 Cranial bones 躯干骨 Trunk bones
附肢骨 Appendicular bones
•成人骨骼有206块命名的骨骼,分为两个主要部分。这些是轴向和附着骨。
•The adult skeleton has 206 named bones divided into two main parts. These are the axial and attachment bones.
轴骨架由围绕轴线的骨骼组成。
附着骨由中轴组外的身体骨骼组成。这些是上肢和下肢。
The axial skeleton consists of the bones surrounding the axis.
The attachment bones consist of the bones of the body outside the axial group. These are the upper and lower limbs.
形态 Shape
长骨: 管状骨 Long bones: tubular bones
短骨: 立方形 Short bones: cubic
扁骨:外板+内板+板障 Flat bones: outer plate + inner plate + lamella
不规则骨:形态不规则 Irregular bones: irregular shapes
长骨,只要它的长度大于它的宽度,就被称为长骨。最明显的长骨在手臂和腿部。
A long bone is called a long bone as long as it is longer than it is wide. The most obvious long bones are in the arms and legs.
短骨的长度、宽度和厚度大致相等,它们发生在手腕和脚踝。
Short bones are roughly equal in length, width, and thickness, and they occur in the wrists and ankles.
扁平的骨头很薄或弯曲,更多时候它们是扁平的。这包括肋骨、肩胛骨、胸骨和颅骨。
Flat bones are thin or curved, and more often they are flat. This includes the ribs, shoulder blades, sternum, and skull.
不规则的骨骼,它们不适合任何其他类别。例如椎骨、面部和髋骨。
Irregular bones, they do not fit into any other category. Examples include vertebrae, face, and hip bones.
2. 骨的构造 Structure of Bones
骨质 Osseous tissue
骨密质 Compact bone
骨松质 Spongy bone
骨 髓 Bone marrow
长骨的骨腔含有黄色骨髓。The bone cavities of long bones contain yellow marrow.
海绵状骨骺充满红色骨髓。The spongy epiphysis is filled with red marrow.
红骨髓: 含造血干细胞 → 造血功能
Red bone marrow: contains hematopoietic stem cells → hematopoietic function
黄骨髓: 被脂肪取代
Yellow bone marrow: replaced by fat
轴向骨骼 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM THE AXIAL SKELETON
颅骨 Cranial Bones
颅骨共有23块,连接形成颅,颅为头面部的骨性支架;可分为脑颅和面颅两部分:
There are 23 skull bones connected together to form the cranium, which is the bony support of the head and face. It can be divided into two parts: the brain skull and the facial skull:
脑颅:围成颅腔, —容纳、保护脑
Cranium: encloses the cranial cavity, which contains and protects the brain
脑颅骨(8块)Skull (8 pieces)
Paired 成对:顶骨 parietal 颞骨 Temporal
Unpaired 不成对:额骨 Frontal 枕骨 Occipital 蝶骨 Sphenoid 筛骨 Ethmoid
面颅: 构成面部支架
Facial skull: forms the framework of the face
眶:容纳眼 Orbit: houses the eyes
骨性鼻腔 Bony nasal cavity
骨性口腔 Bony oral cavity
面颅骨 (15块)
Facial skull bones (15 pieces)
Paired 成对:上颌骨 maxilla 颧骨 zygomaticus 鼻骨 Nasal 泪骨 Lacrimal
Unpaired 腭骨 Palatal 下鼻甲 Inferior turbinate
不成对:下颌骨 mandible 舌骨 hyoid 犁骨 vomer
体表标记:Body landmarks:
枕骨粗隆 Occipital protuberance
颞骨乳突 Temporal mastoid process
新生儿颅的特征 Characteristics of the newborn skull
1.与躯干比较,新生儿颅的体积相对较大
1. Compared with the trunk, the newborn skull is relatively large
2.新生儿脑颅与面颅相比,脑颅比例相对较大(8:1)
2. Compared with the facial skull, the ratio of the newborn skull to the facial skull is relatively large (8:1)
3.颅盖骨间为膜性连接,交界处的间隙称囟门
3. The skull bones are connected by membranes, and the gap at the junction is called the fontanelle
前囟:最大,1-2岁闭合 Anterior fontanelle: the largest, closed at 1-2 years old
后囟 Posterior fontanelle
蝶囟 Sphenoid fontanelle
乳突囟 Mastoid fontanelle
一.椎骨 1. Vertebrae
颈椎 (Cervical vertibrae): C1-C7
胸椎 (Thoracic vertebrae): T1-T12
腰椎(Lumbar vertibrae): L1-L5
1.椎骨的一般形态: 椎体 + 椎弓
1. General morphology of vertebrae: Vertebral body + vertebral arch
典型椎骨 Typical vertebra
•虽然大小和形状有差异,但不同区域的椎骨结构基本相似。
• Although there are differences in size and shape, the structure of vertebrae in different regions is basically similar.
它由椎体,椎弓和七个突起组成。
It consists of the vertebral body, vertebral arch, and seven processes.
•体厚,圆盘形,位于前部。它具有上部和下部粗糙区域,用于与椎间盘连接。
• The body is thick, disc-shaped, and located in the front. It has upper and lower rough areas for connection with the intervertebral disc.
椎弓从椎骨体向后延伸。它围绕着脊髓。位于椎弓和身体之间的空间称为椎孔,在椎孔内容纳脊髓。
所有椎骨的椎骨孔共同形成椎管。
The vertebral arch extends backward from the vertebral body. It surrounds the spinal cord. The space between the vertebral arch and the body is called the vertebral foramen, which contains the spinal cord.
The vertebral foramina of all vertebrae together form the vertebral canal.
脊柱 Spine
•椎体柱与胸骨和肋骨一起构成了身体躯干的骨架。它占身体高度的2/5,男性的平均长度为71厘米,女性
• The vertebral column, together with the sternum and ribs, forms the skeleton of the body's trunk. It accounts for 2/5 of the body's height and has an average length of 71 cm for males and 61 cm for females.为61厘米。
成人椎体柱包含26个椎骨。
它对任一方向和旋转都非常强大和灵活。包围和保护脊髓,支撑头部,并作为背部肋骨和肌肉的附着点。
The adult vertebral column contains 26 vertebrae.
It is very strong and flexible for either orientation and rotation. It surrounds and protects the spinal cord, supports the head, and serves as an attachment point for the ribs and muscles of the back.
•从侧面看时,椎体不是直线,而是有曲线。这些是椎体的正常曲线。椎骨形成4条曲线,两条是凹的,另外两条是凸的。曲线的存在有几个功能;能够吸收冲击,保持平衡,保护脊柱免受断裂和增加柱的强度。
• When viewed from the side, the vertebrae are not straight, but have curves. These are the normal curves of the vertebrae. The vertebrae form 4 curves, two are concave and the other two are convex. The presence of the curves has several functions; the ability to absorb shock, maintain balance, protect the spine from fractures and increase the strength of the column.
2. 各部椎骨的主要特征
2. Main features of each vertebra
体表标记:Surface markings:
第七颈椎
Seventh cervical vertebra
颈椎Cervical | 胸椎Thoracic | 腰椎Lumbar | |
|---|---|---|---|
椎体 Body | 小 Small | 较大 Larger | 最大 Maximum |
棘突 Spinous process | 短、末端分叉 Short, split ends | 最长、倾向后下Longest, tends to be backward and downward | 短、板状水平后伸Short, plate-like horizontal extension |
三.胸骨与肋 Sternum and Ribs
胸骨:Sternum:
•胸骨是扁平的窄骨,长约 15 厘米(6 英寸),位于胸前壁的正中线。它由3个基本部分组成:胸骨柄(上部),胸骨体(中部和最大部分)和剑突(下部和最小部分)。
胸骨柄和胸骨体的交界处形成胸骨角。胸骨柄的上方有一个凹陷,称为胸骨上切口。
胸骨柄与第一和第二肋骨相连。胸骨体直接或间接与第 2 至 10 根肋骨相连。
•The sternum is a flat, narrow bone, about 15 cm (6 in) long, located in the midline of the anterior chest wall. It consists of 3 basic parts: the manubrium (upper part), the body (middle and largest part), and the xiphoid process (lower and smallest part).
The junction of the manubrium and the body forms the sternal angle. There is a depression above the manubrium, called the suprasternal notch.
The manubrium is connected to the first and second ribs. The body of the sternum is directly or indirectly connected to the 2nd to 10th ribs.
肋:肋骨 + 肋软骨
1-7肋 ----- 真肋
8-10肋 ---- 假肋
11-12肋 --- 浮肋
Ribs: ribs + costal cartilage
Ribs 1-7 - True ribs
Ribs 8-10 - False ribs
Ribs 11-12 - Floating ribs
体表标记:Body landmarks:
胸骨角 Sternal angle
第十一肋骨头 Eleventh rib head
第十二肋骨头 Twelfth rib head
•人类包含12对肋骨,构成胸腔的一侧。肋骨的长度从第1到第7个增加,从第7个到第12个长度减少。
在前面,第一到第七根肋骨通过肋软骨直接附着在胸骨上,因此它们被称为真肋骨。
第 8 – 10 根肋骨,它们是一组假肋骨,它们的软骨相互连接,然后附着在第 7 根肋骨的软骨上。第11和第12肋骨被指定为浮动肋骨,因为它们的前部甚至不会间接附着在胸骨上。
•Humans contain 12 pairs of ribs that make up one side of the thoracic cavity. The length of the ribs increases from the 1st to the 7th and decreases from the 7th to the 12th.
In front, the 1st to 7th ribs are directly attached to the sternum through the costal cartilages, so they are called true ribs.
The 8th – 10th ribs, which are a set of false ribs, have their cartilages connected to each other and then attached to the cartilage of the 7th rib. The 11th and 12th ribs are designated as floating ribs because their front parts are not even indirectly attached to the sternum.
附肢骨骼 THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON
1. 分类: 肢带骨 自由肢骨
1. Classification: Limb girdle bones Free limb bones
2. 上、下肢骨骼的配布:基本对称
2. Distribution of upper and lower limb bones: basically symmetrical
3. 上、下肢骨骼的特点:
3. Characteristics of upper and lower limb bones:
上肢骨轻巧、关节灵活 适应操纵劳动工具
Upper limb bones are light and flexible in joints, suitable for manipulating labor tools
下肢骨粗壮、关节稳固 适应负重与直立行走
Lower limb bones are strong and stable in joints, suitable for weight bearing and upright walking
上肢带骨 :锁骨 肩胛骨 Bones of upper limb girdle: clavicle, scapula
锁骨: 胸骨端 肩峰端 Clavicle: sternal end, acromion end
肩胛骨:两面: 前面:肩胛下窝。后面:肩胛冈 肩峰 冈上窝、冈下窝
三缘:上缘:肩胛切迹 喙突;内侧缘(脊柱缘);外侧缘(腋缘)
三角:上角; 下角--平对第7肋/肋间隙; 外侧角:关节盂
Scapula: two sides: front: subscapular fossa. Back: scapular spine, acromion, supraspinous fossa, infraspinous fossa
Three edges: upper edge: scapular notch, coracoid process; medial edge (vertebral margin); lateral edge (axillary margin)
Triangle: upper angle; lower angle--opposite to the 7th rib/intercostal space; lateral angle: glenoid
上肢自由肢骨:肱 (Gōng)骨 尺骨和桡(Ráo)骨 腕骨 掌骨 指骨
肱骨:肱骨头 肱骨体: 肱骨小头 肱骨滑车 鹰嘴窝 内、外上髁
桡骨:桡骨头 桡骨茎突 腕关节面 尺切迹
Free limb bones of upper limb: humerus, ulna and radius, carpal bones, metacarpal bones, phalanges
Humerus: humeral head, humeral body: humeral capitulum, humeral trochlea, olecranon fossa, medial and lateral epicondyle
Radius: radial head, radial styloid process, wrist joint surface, ulnar notch
下肢带骨: 髋(Kuān)骨
髋骨:
髂(Qià)骨:髂嵴, 髂前、后上棘, 髂前、后下棘
坐骨: 坐骨结节
耻骨:耻骨联合
Bones of the lower limb girdle: Hip bone
Hip bone:
Iliac bone: Iliac crest, anterior and posterior superior iliac spines, anterior and posterior inferior iliac spines
Ischia: Ischial tuberosity
Pubic bone: Pubic symphysis
下肢自由肢骨:股骨 髌骨 胫骨 和腓骨 跗(Fū)骨 跖(Zhí)骨 趾(Zhǐ)骨
股骨:股骨头 股骨颈 大转子 内侧髁 外侧髁
髌骨
胫骨:胫骨粗隆 内踝
腓骨:腓骨头 外踝
Bones of the lower limb: femur, patella, tibia and fibula, tarsal bones, metatarsal bones and phalanges
Femur: femoral head, femoral neck, greater trochanter, medial condyle and lateral condyle
Patella
Tibia: tibial tuberosity and medial malleolus
Fibula: fibular head and lateral malleolus
跗骨:距骨 足舟骨 跟骨 骰骨 内侧、中间、外侧楔骨
口诀:距在上,跟在下, 距前舟,跟前骰,内中外楔并排走
跖骨 5
趾骨 14 近、中、远节趾骨
Tarsal bones: talus, navicular bone, calcaneus, cuboid bone, medial, middle and lateral cuneiform bones
Mnemonic formula: talus is on top, heel is on the bottom, talus anterior navicular bone, heel anterior cuboid bone, medial, middle and lateral cuneiform bones go side by side
Metatarsal bones 5
Phalans 14 proximal, middle and distal phalanges
肌肉系统 Muscular system
概述
一、肌肉的组织构造分类
二、骨骼肌的构造和分类
三、肌的起、止点和功能
四、肌的命名
Overview
1. Classification of muscle tissue structure
2. Structure and classification of skeletal muscle
3. Origin, insertion and function of muscle
4. Naming of muscle
一、肌肉的组织构造分类
分类 分布 神经支配
平滑肌(内脏肌、不随意肌) 内脏、血管壁 内脏神经
心肌(不随意肌、横纹肌) 心脏壁 内脏神经
骨骼肌(随意肌、横纹肌) 头、躯干、四肢 躯体神经
1. Classification of muscle tissue structure
Classification Distribution Innervation
Smooth muscle (visceral muscle, involuntary muscle) Visceral, blood vessel wall Visceral nerve
Myocardial muscle (involuntary muscle, striated muscle) Heart wall Visceral nerve
Skeletal muscle (voluntary muscle, striated muscle) Head, trunk, limbs Somatic nerve
二、骨骼肌的构造和分类
2. Structure and classification of skeletal muscle
(一)肌的构造
肌腹 色红质软 肌纤维 有收缩力
肌腱 色白较硬 胶原纤维 无收缩力
(I) Structure of muscle
Muscle belly Red and soft Muscle fiber Contractile
Tendon White and hard Collagen fiber No contractile force
(二)肌的形态分类
分类位置功能
长肌四肢引起大幅度运动
短肌躯干部深层产生小幅度运动
维持身体姿势
阔肌胸腹壁多种形式运动保护内脏
轮匝肌肉孔裂周围关闭孔裂
(II) Classification of muscle morphology
Classification position function
Long muscles cause large-scale movements in the limbs
Short muscles produce small-scale movements in the deep layer of the trunk
Maintain body posture
Broad muscles of the chest and abdominal wall move in various forms to protect internal organs
Orbicularis muscles close the foramen around the foramen
三、肌的起止点、和作用
肌的起止
肌在固定骨上的附着点称为肌的起点或定点
肌在移动骨上的附着点称为肌的止点或动点
起点Origin:• 肌肉的一端由肌腱连接到保持相对稳定的骨骼上,通常更接近身体的中线。•
止点Insertion:• 肌肉另一端的肌腱附着在肌肉移动的骨骼上.
III. Origin and insertion of muscles, and their functions
Origin and insertion of muscles
The attachment point of a muscle on a fixed bone is called the origin or fixed point of the muscle
The attachment point of a muscle on a moving bone is called the insertion or moving point of the muscle
Origin:• One end of a muscle is connected to a relatively stable bone by a tendon, usually closer to the midline of the body. •
Insertion:• The tendon at the other end of the muscle is attached to the bone that the muscle moves.
四、肌的命名原则
形状:斜方肌,三角肌
位置:冈上肌,骨间肌
形态结构和部位:肱三头肌
大小和位置:腰大肌
起点:胸锁乳突肌, 胸骨舌骨肌
作用:旋后肌,
位置和肌的方向:腹外斜肌, 腹横肌
IV. Principles of muscle naming
Shape: trapezius, deltoid
Location: supraspinatus, interosseous
Morphological structure and location: triceps
Size and location: psoas
Starting point: sternocleidomastoid, sternohyoid
Action: supinator,
Location and direction of muscle: external oblique, transverse abdominis
肌肉:
头部肌肉
颈部肌肉
躯干肌
背肌
胸肌
腹肌
肩部肌肉
•上臂肌肉•前臂肌肉
臀部肌肉
•大腿肌肉•小腿肌肉
Muscles:
Head muscles
Neck muscles
Trunk muscles
Back muscles
Chest muscles
Abdominal muscles
Shoulder muscles
•Upper arm muscles•Forearm muscles
Buttocks muscles
•Thigh muscles•Calf muscles
头肌 Muscles of Head
一、Facial Muscles 面肌
(一)Epicranius颅顶肌
枕额肌 Occipitofrontal muscle
帽状腱膜 Galea aponeurosis
额腹 Frontal belly
枕腹 Occipital belly
(二)眼轮匝肌 Orbicularis oculi muscle
(三)口周围肌 Perioral muscle
二、Masticatory Muscles 咀嚼肌
咬肌、颞肌、翼外肌和翼内肌。
masseter, temporalis, lateral pterygoid and medial pterygoid muscles.
颈肌 Muscles of Neck
胸锁乳突肌 Sternocleidomastoid muscle
位置:斜列于颈部两侧 Location: obliquely arranged on both sides of the neck
作用:一侧肌收缩使头向同侧倾斜,脸转向对侧;两侧收缩可使头后仰。
Function: Contraction of one side of the muscle causes the head to tilt to the same side and the face to turn to the opposite side; contraction of both sides can cause the head to tilt back.
躯干肌 Trunk muscles
一、背肌 1. Back muscles
(一)Trapezius 斜方肌
位于项部和背上部的浅层
Superficial layer located at the nape and upper back
(二)Latissimus Dorsi背阔肌
位于背的下半部及胸的后外侧
Located on the lower back and the posterior and lateral sides of the chest
(三)Erector Spinea竖脊肌
纵列于躯干的背面,脊柱两侧的沟内。
They are located vertically on the back of the trunk, in the grooves on both sides of the spine.
二、Muscles of Thorax 胸肌
胸肌可分为胸上肢肌和胸固有肌。
The chest muscles can be divided into the upper limb muscles and the intrinsic chest muscles.
(一)胸上肢肌
(I) Upper limb muscles
1、胸大肌 Pectoralis Major
位置:覆盖胸廓前壁的大部,呈扇形。
Location: Covers most of the anterior wall of the thorax and is fan-shaped.
2、胸小肌 Pectoralis minor
3、前锯肌 Serratus Anterior
(二)胸肌 Chest muscles
1、IntercostalesExterni肋间外肌,位于各肋间隙的浅层,能提肋助吸气。
2、IntercostalesInterni肋间内肌,位于肋间内肌的深面,可降肋助呼气。
三、Diaphrgam膈
位置:位于胸腹腔之间,成为胸腔的底和腹腔的顶。
Located between the thoracic and abdominal cavities, forming the bottom of the thoracic cavity and the top of the abdominal cavity.
Muscles of breathing 呼吸肌肉
Diaphragm (隔膜)
External intercostalmuscles (肋间外肌)
Internal intercostalmuscles (肋间内肌)
Muscles of the Abdomen 腹肌
•External oblique (外斜肌)
•Internal oblique (内斜肌)
•Transversusabdominis(腹横肌)
•Rectus abdominis (腹直肌)
•Linea alba (connective tissue) (腹白线)
1、Obliquus Externus Abdominis 腹外斜肌
位于腹前外侧部的浅层
Superficial layer located in the anterolateral part of the abdomen
2、Obliquus Internus Abdominis 腹内斜肌
在腹外斜肌深面
Deep to the external oblique muscle
3、Transversus Abdominis 腹横肌
在腹内斜肌深面
Deep to the internal oblique muscle
4、Rectus Abdominis 腹直肌
位于腹前壁正中线的两旁
Located on both sides of the midline of the anterior abdominal wall
肩部肌肉及前臂肌 Shoulder and forearm muscles
•Deltoid 三角肌 位于肩部,呈三角形。
•Biceps Brachii 肱二头肌
•Triceps Brachii 肱三头肌
•Flexor carpiradialis(桡侧腕屈肌)
•Flexor carpiulnaris(尺侧腕屈肌)
•Palmaris longus (掌长肌)
•Extensor carpiradialislongus(桡侧腕长伸肌)
•Extensor carpiradialisbrevis(桡侧腕短伸肌)
•Extensor carpiulnaris(尺侧腕伸肌)
•Extensor(趾伸肌)
Buttocks (臀部肌)
•Gluteus maximus(臀大肌)
•Gluteus medius(臀中肌)
•Gluteus minimus(臀小肌)
Muscles of the Thigh (大腿肌肉)
(一)前群 Front Group
Sartorius(缝匠肌)
Quadriceps femoris (股四头肌):
Rectus femoris(股直肌)
Vastus lateralis(股外侧肌)
Vastus medialis(股内侧肌)
Vastus intermedius(股中间肌)
(二)后群 Hamstring muscles (腿后肌群)
Semimembranosus(半膜肌)
Semitendinosus(半腱肌)
Biceps femoris(股二头肌)
Muscles of the Lower Leg 小腿肌肉(前群)
Tibialisanterior(胫骨前肌)
Extensor digitorum longus (趾长伸肌)
Muscles of the Lower Leg 小腿肌肉(后群)
•Triceps surae(小腿三头肌)
Gastrocnemius(腓肠肌)
Achilles tendon (跟腱)
Soleus (比目鱼肌)
骨连接 Joints
骨连接Joints--是骨与骨之间的连接装置,可分为两大类:
一、直接连接 - 相连的骨之间无腔隙
纤维连结: 骨与骨之间由纤维组织相连
软骨连结: 骨与骨之间由软骨相连
骨性结合: 由纤维连结或软骨连接骨化形成
二、间接连接——滑膜关节Synovial Joint
骨与骨之间借内衬滑膜的结缔组织囊相连,其间有腔隙存在,使连结的骨块之间能进行运动。(多数位于四肢关节)
Joints--are the connecting devices between bones, which can be divided into two categories:
1. Direct connection-no cavity between connected bones
Fibrous connection: bones are connected by fibrous tissue
Cartilage connection: bones are connected by cartilage
Osteosynthesis: formed by ossification of fibrous connection or cartilage connection
2. Indirect connection-Synovial Joint
Bones are connected by connective tissue capsules lined with synovium, and there are cavities between them, so that the connected bones can move. (Mostly located in the joints of the limbs)
(1)基本构造
1.关节面Articular Surface
关节头
关节窝
2.关节囊Articular Capsule
纤维膜
滑膜
3.关节腔Articular Cavity
(1) Basic structure
1. Articular surface
Articular head
Articular fossa
2. Articular capsule
Fibrous membrane
Synovium
3. Articular cavity
(2)关节的辅助结构:参与关节的构成但并非所有关节都有的结构:
(2) Auxiliary structures of joints: structures that participate in the formation of joints but are not present in all joints:
韧带:连接相邻骨之间的致密结缔组织束 —增加稳固性
囊外韧带 / 囊内韧带
Ligaments: dense connective tissue bundles that connect adjacent bones - increase stability
Extracapsular ligaments / intracapsular ligaments
关节盘:位于相对关节面间的纤维软骨板 — 改善关节面之间的适配度、减少冲力
Articular disc: fibrous cartilage plate located between the opposing joint surfaces - improves the fit between the joint surfaces and reduces impact
躯干骨的连结
Trunk bone connection
椎骨的连结
(1)椎体间的连结
(2)椎弓间的连结
Connections between vertebrae
(1) Connections between vertebral bodies
(2) Connections between vertebral arches
颅骨的连结
颞下颌关节
Skull joints
Temporomandibular joint
上肢骨的连结 Joints of upper limb bones
(1)胸锁关节:由胸骨的锁切迹和锁骨的胸骨端构成。该关节能使锁骨小幅度运动。
(2)肩锁关节:由肩胛骨的肩峰与锁骨的肩峰端构成,属微动关节。
(3)肩关节:由肩胛骨的关节盂和肱骨头构成。
(4)肘关节
(1) Sternoclavicular joint: It is composed of the clavicular notch of the sternum and the sternal end of the clavicle. This joint allows the clavicle to move slightly.
(2) Acromioclavicular joint: It is composed of the acromion of the scapula and the acromion end of the clavicle. It is a micro-motion joint.
(3) Shoulder joint: It is composed of the glenoid cavity of the scapula and the head of the humerus.
(4) Elbow joint
2.下肢骨的连结
(1)髋骨的连结
(2)髋关节
(3)膝关节
2. Connections of lower limb bones
(1) Connections of hip bones
(2) Hip joint
(3) Knee joint
感觉器官 Sense organs
感受细胞连同其附属结构组成了感觉器官,如眼、耳、鼻等
Receptor cells and their accessory structures make up sense organs, such as eyes, ears, nose, etc.
眼eye

眼球:
眼球壁
眼球内容物
眼睑
结膜
泪器
眼球外肌
Eyeball:
Eyeball wall
Eyeball contents
Eyelid
Conjunctiva
Tear apparatus
Extraocular muscles

视杆细胞(暗视力)
视锥细胞(明视力)
视神经盘 (生理盲点):是视神经和视网膜血管出入口
黄斑(感光敏锐)
◆位于视神经盘的颞下方约3.5 mm处
◆又称中央凹, 无血管,视锥细胞多,无视杆细胞,故感光最敏锐
Rods (dark vision)
Cones (bright vision)
Optic disc (physiological blind spot): the entrance and exit of the optic nerve and retinal blood vessels
Macula (photosensitive)
◆Located about 3.5 mm below the temporal part of the optic disc
◆Also known as the fovea, no blood vessels, many cones, no rods, so the most sensitive to light
耳 ear
◆听觉感受器——感受声音
◆Auditory receptors - sense sound
◆位觉感受器——感受头部位置变动和运动速度等
◆Position receptors - sense changes in head position and movement speed, etc.

•Outer Ear 外耳
•Middle Ear中耳
•Inner Ear 内耳
•Outer Ear 外耳:
Auricle(Pinna)耳廓
External Auditory canal 外耳道
Tympanic membrane 鼓膜
•Middle Ear中耳:
Three bones–malleus锤骨, incus砧骨, stapes镫骨
Eustachian tube 咽鼓管–pharynx咽
Oval Window 椭圆窗
•Inner Ear 内耳:
Cochlea 耳蜗
Semi circular canals 半规管

内分泌系统
endocrine system神经系统nervous system
心血管系统cardiovascular system
呼吸系统respiratory system
消化系统digestive system
泌尿系统urinary system
内分泌系统 Endocrine system
内分泌系统是由腺体组成的, 每个腺体都分泌不同 类型的激素,直接进⼊⾎液以维持体内平衡。
The endocrine system is made up of glands, each of which secretes different types of hormones directly into the bloodstream to maintain homeostasis in the body.
内分泌系统 ·松果体 ·垂体 ·甲状腺 ·甲状旁腺 ·胰岛 ·肾上腺 ·性腺 ·卵巢(⼥性) ·睾丸(男)
Endocrine system ·Pineal gland ·Pituitary gland ·Thyroid gland ·Parathyroid gland ·Pancreatic islets ·Adrenal glands ·Gonads ·Ovaries (female) ·Testicles (male)
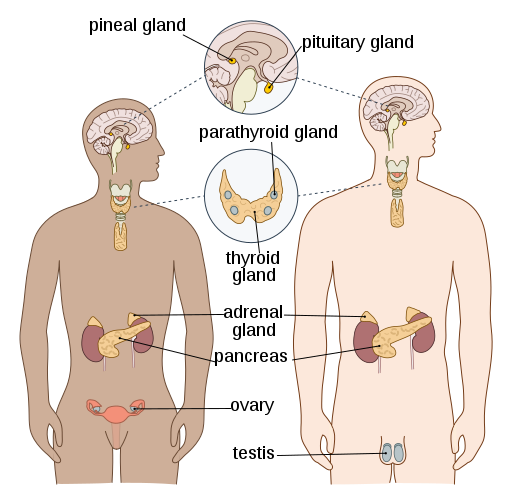
松果体, ⼀个⼩的, 扁平 的, 锥形的位于丘脑两部分之 间的结构,在许多动物和⼈类 中产⽣⼀种激素,称为 褪⿊激 素。
The pineal gland, a small, flat, cone-shaped structure located between two parts of the thalamus, produces a hormone called melatonin in many animals and humans.
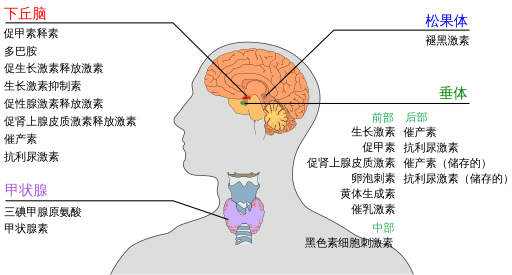
垂体 ·垂体位于⼤脑底部,位于 蝶⻣内。
垂体激素
·垂体前叶
⼈类⽣⻓激素 (HGH)
促甲状腺激素 (TSH)
促肾上腺⽪质激素 (ACTH)
催乳素 (PRL)
促卵泡激素 (FSH)
⻩体⽣成素 (LH)
·垂体后叶
抗利尿激素(ADH)
催产素 (OT)
Pituitary gland · The pituitary gland is located at the base of the brain, inside the sphenoid bone.
Pituitary hormones
· Anterior pituitary gland
Human growth hormone (HGH)
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
Adrenocortical stimulating hormone (ACTH)
Prolactin (PRL)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
· Posterior pituitary gland
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Oxytocin (OT)
松果体 脑垂体
甲状腺
甲状腺 是⼀个双叶器官, 覆盖在⽓管前⽅。
甲状腺激素
·甲状腺素 T4
·三碘甲状腺原氨酸 T3 ·
降钙素
Thyroid gland
The thyroid gland is a bilobed organ that covers the front of the trachea.
Thyroid hormones
· Thyroxine T4
· Triiodothyronine T3 ·
Calcitonin
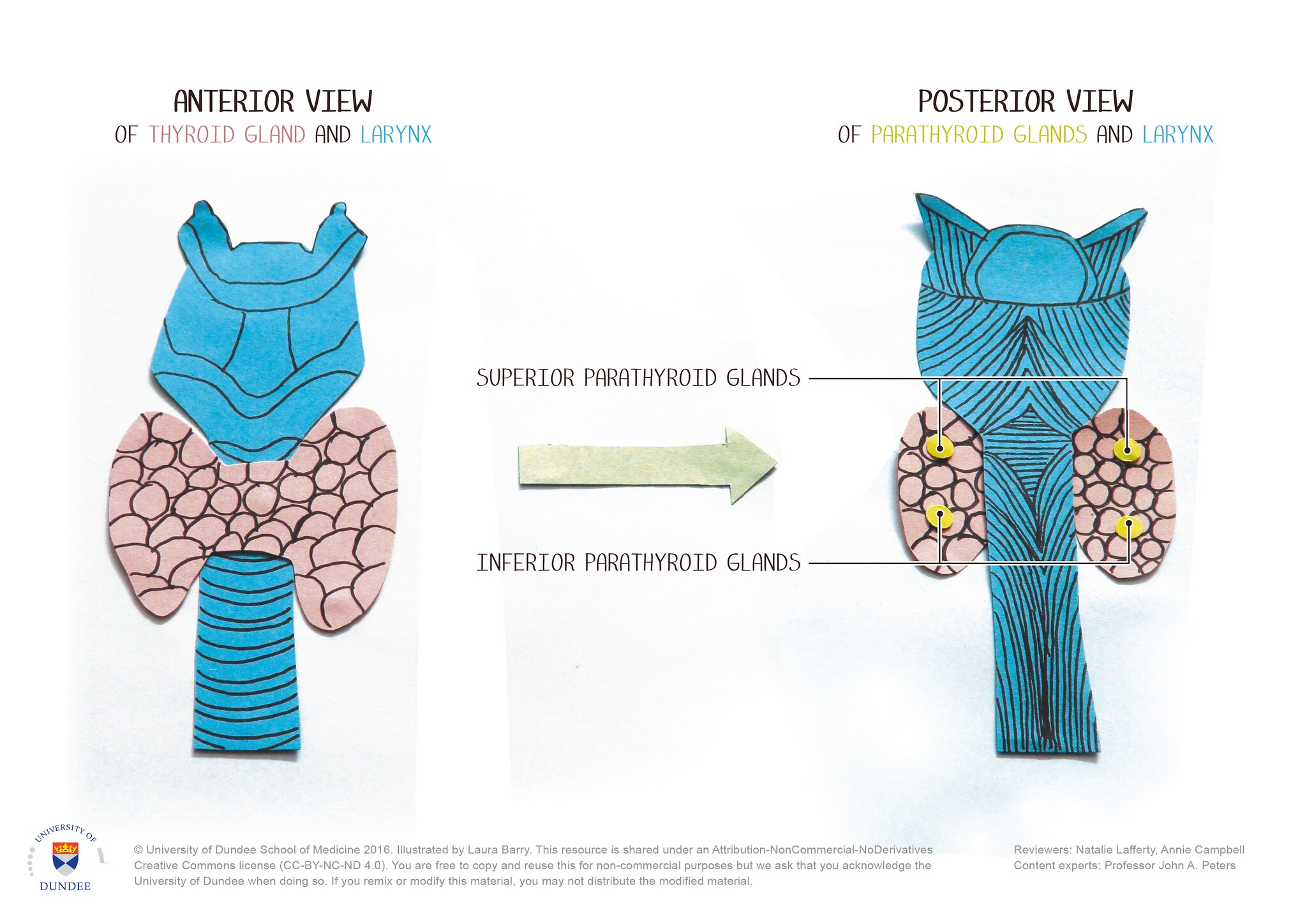
甲状旁腺 Parathyroid glands
·甲状旁腺通常有四个, 嵌⼊甲状腺的背⾯。
甲状旁腺激素 ·甲状旁腺激素
· There are usually four parathyroid glands, embedded in the back of the thyroid gland.
Parathyroid hormone · Parathyroid hormone
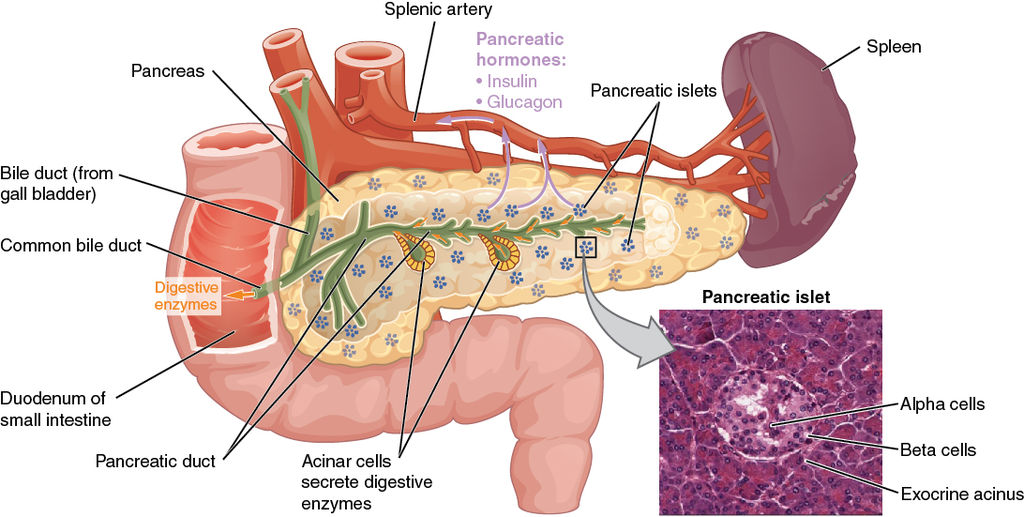
胰岛 ·胰腺的内分泌功能由胰岛执⾏——⼩的、⾼度⾎管化的 细胞团散布在整个胰腺中, 仅占整个器官的 1% ⾄ 3%。
Islets of Langerhans · The endocrine functions of the pancreas are performed by islets of Langerhans—small, highly vascularized cell clusters scattered throughout the pancreas that make up only 1% to 3% of the entire organ.
胰岛激素 Islet Hormones
·胰岛素-β细胞 · Insulin—beta cells
·胰⾼⾎糖素 (胰腺⾼⾎糖素)—阿尔法细胞
· Glucagon (pancreatic glycogen)—alpha cells
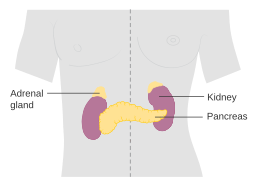
肾上腺 ·肾上腺是成对的⻩⾊组 织块,位于每个肾脏的上 极。
每个腺体由两个不同的部 分组成——肾上腺⽪质 (位于外侧)和肾上腺髓 质(位于内侧)。
Adrenal Glands · The adrenal glands are paired yellow masses of tissue located at the upper pole of each kidney.
Each gland is made up of two distinct parts – the adrenal cortex (on the outside) and the adrenal medulla (on the inside).
肾上腺激素
·⽪质 ——
·盐⽪质激素
·糖⽪质激素
·类固醇激素
·髓质 (髓质)——
·肾上腺素
·去甲肾上腺素
性腺
女性的性腺是卵巢
男性的性腺是睾丸
·卵巢: ·雌激素 ·⻩体酮
·睾丸 ·睾酮
Adrenal hormones
·Cortex ——
·Mineral corticosteroids
·Glucocorticoids
·Steroid hormones
·Medulla (medulla)——
·Epinephrine
·Norepinephrine
Gonads
The female gonads are ovaries
The male gonads are testicles
·Ovaries: ·Estrogen ·Ovarian hormones
·Testicles ·Testosterone
NERVOUS SYSTEM 神经系统
神经系统是机体内的主导系统,由脑、脊髓以及与它们相连的周围神 经构成;它对机体各系统起控制和协调作用,使机体能随内外环境的变化 做出适应性反应
The nervous system is the dominant system in the body, consisting of the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves connected to them; it controls and coordinates the various systems of the body, enabling the body to respond adaptively to changes in the internal and external environment.
Nervous_system_神经系统
●中枢神经系统: 脑 脊髓
Central nervous system: brain spinal cord
周围神经系统: 12对颅神经 31对脊神经
Peripheral nervous system: 12 pairs of cranial nerves 31 pairs of spinal nerves
●神经元(神经细胞)
Neurons (nerve cells)
●神经细胞提供神经系统的大部分独特功能
Nerve cells provide most of the unique functions of the nervous system
●神经胶质细胞 支持、滋养和保护神经元.神经胶质或神经胶质比神 经元小,比神经元多5到50倍。
●Glial cells support, nourish and protect neurons. Glia or neuroglia are smaller than neurons and are 5 to 50 times more numerous than neurons.
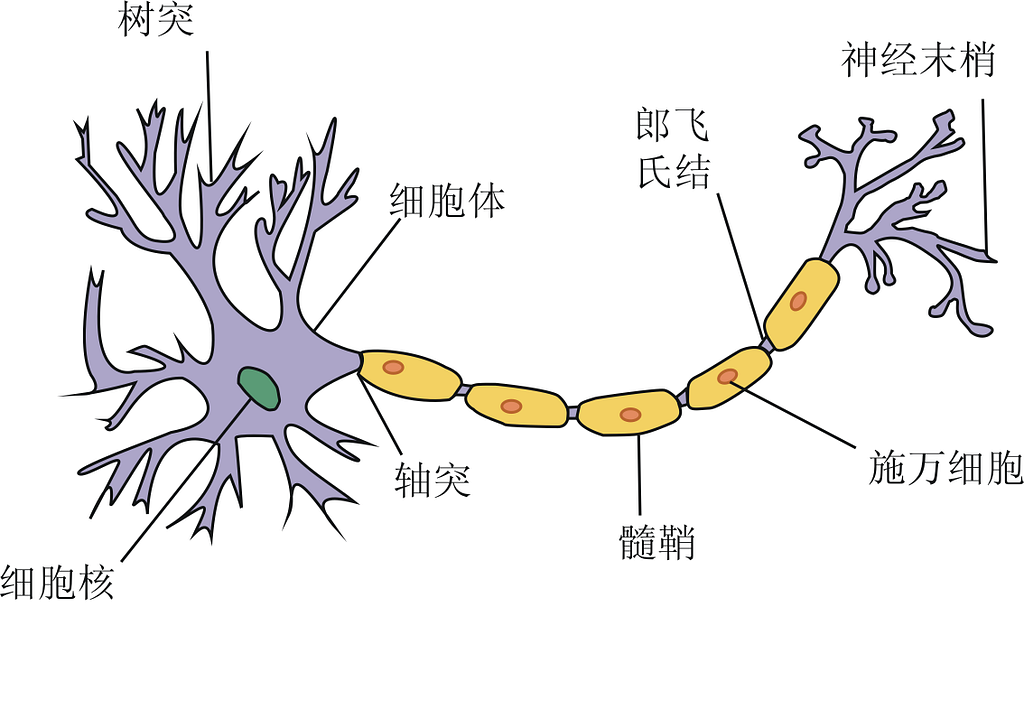
●神经元(神经细胞)
Neurons (nerve cells)
(1)细胞体——细胞核、细胞质、细胞器等
(1) Cell body - nucleus, cytoplasm, organelles, etc.
(2)树突(树突) - 接收或输入神经元的部分
(2) Dendrites (Dendrites) - the receiving or input part of a neuron
(3)轴突通过煤介传送神经冲动向另一个神经元、 肌纤维或腺体细胞传播。 神经细胞的组成部分 由多层脂质和蛋白质覆盖物包围的轴突被称为髓鞘。 没有这种覆盖物的轴突是无髓鞘的 髓鞘)
(3) The axon transmits the nerve impulse through the media to another neuron, muscle fiber, or gland cell. The axon is surrounded by a multilayered covering of lipids and proteins called the myelin sheath. An axon without this covering is unmyelinated.
●中枢神经系统
Central nervous system
脑:在大脑中,一层薄薄的灰质覆盖着大脑最大部分,大脑和小脑的表面。
●外部部分 - 灰质 内部 – 白质
○ 脊髓:在脊髓中,白质围绕灰质的内核。它的形状像蝴蝶或字母H;
○外部部分 - 白质 内部 – 灰质
Brain: In the brain, a thin layer of gray matter covers the surface of the largest parts of the brain, the cerebrum and cerebellum.
● External part - gray matter Internal - white matter
○ Spinal cord: In the spinal cord, white matter surrounds an inner core of gray matter. It is shaped like a butterfly or the letter H;
○ External part - white matter Internal - gray matter
白质主要由有髓鞘轴突组成。髓磷脂的白色使白质得名。 灰质包含神经细胞体、树突、无髓鞘轴突、轴突末梢和神 经胶质细胞。它看起来是灰色的,而不是白色的。 血管存在于白质和灰质中。
White matter consists mainly of myelinated axons. The white color of myelin gives white matter its name. Gray matter contains nerve cell bodies, dendrites, unmyelinated axons, axon terminals, and glial cells. It appears gray, not white. Blood vessels are present in both white and gray matter.
脑的区分
Brain division
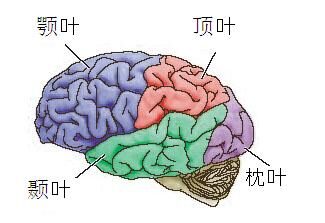
大脑
Cerebrum
■左半球 右半球 (通过胼胝体连接 )
■Left hemisphere Right hemisphere (connected by corpus callosum)
额叶 Frontal lobe
顶叶 Parietal lobe
颞叶 Temporal lobe
枕叶 Occipital lobe
脑干 Brainstem
● 丘脑-下丘脑 - 脑垂体
● Thalamus-Hypothalamus-Pituitary
● 中脑
● Midbrain
● 脑桥
● Pons
● 延髓
● Medulla oblongata
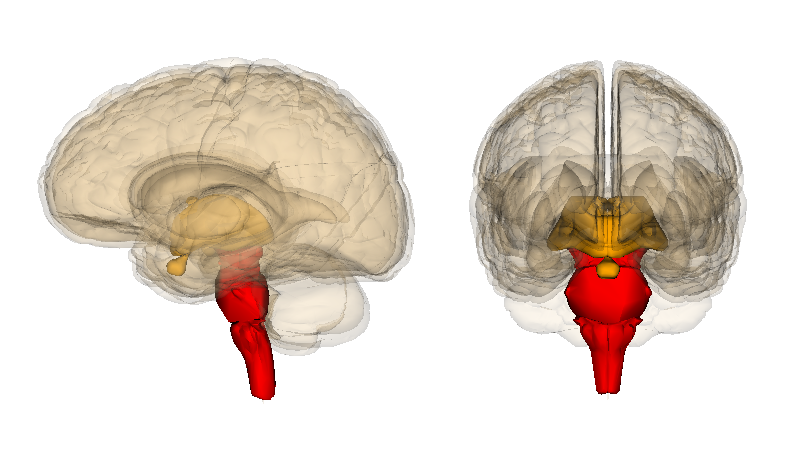
小脑
Cerebellum
● 脑膜
● Meninges
硬脑膜 Dura mater
蛛网膜 Arachnoid mater
软脑膜 Pia mater
脑脊液填充大脑和脊髓中软脑膜和蛛网膜之间的蛛网膜下腔空间。脑脊液也填充大脑中称为脑室的空间。
CSF fills the subarachnoid space between the pia mater and arachnoid membrane in the brain and spinal cord. CSF also fills spaces in the brain called ventricles.
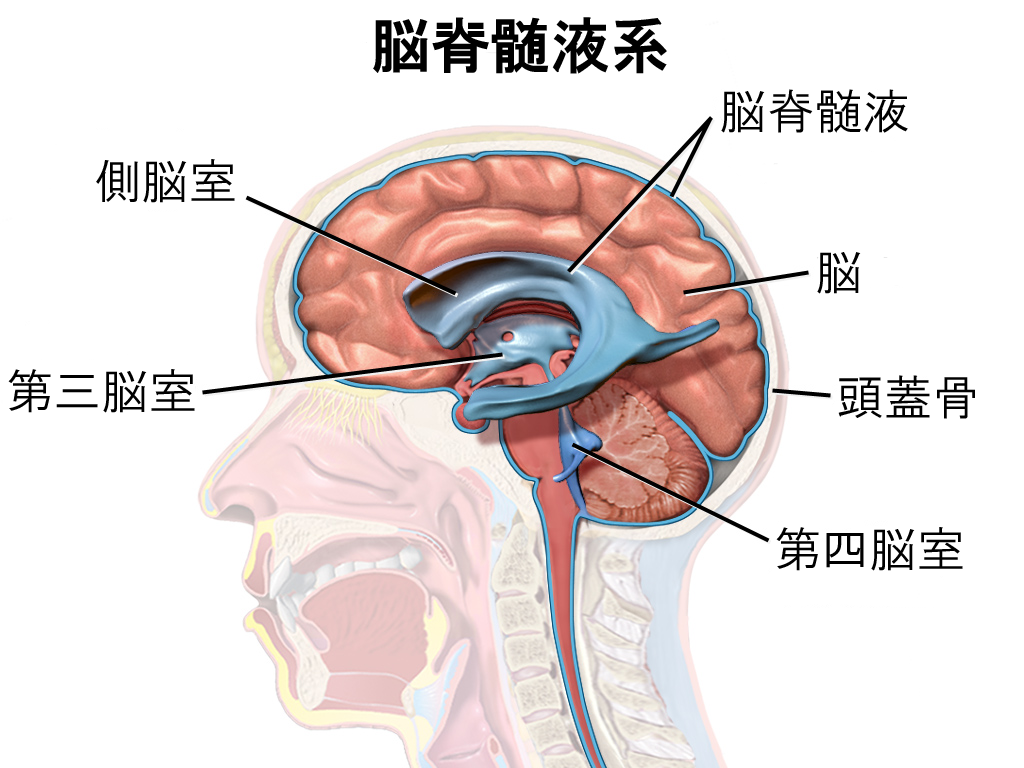
脑室
脊髓节段 ⎯ 与每一对脊神经相连 的脊髓的一段称为一个脊髓节段;
共31个节段
脊髓下端 ⎯ (成人) 第1腰椎下缘
Spinal cord segment ⎯ A section of the spinal cord connected to each pair of spinal nerves is called a spinal cord segment;
31 segments in total
Lower end of the spinal cord ⎯ (Adult) Lower edge of the first lumbar vertebra
脊髓横断面
脊髓的内部结构 ― 灰质 (Grey matter) 灰 质
Internal structure of the spinal cord - Grey matter Grey matter
脊髓的内部结构―白质(White matter) 上行下行的神经纤维束
Internal structure of the spinal cord - White matter Ascending and descending nerve fiber bundles
●脑膜也向下延伸并围绕形成脊髓周围保护层。
●The meninges also extend downward and surround the spinal cord to form a protective layer.
• 周围神经系统
• Peripheral nervous system
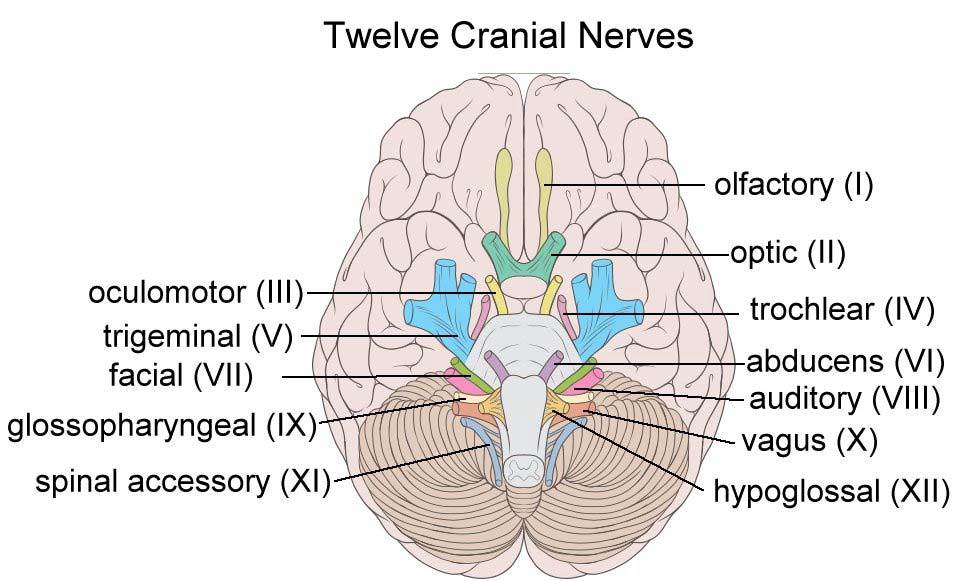
–12对颅神经
–12 pairs of cranial nerves
脑神经的顺序及名称:
Ⅰ 嗅神经 olfactory
Ⅱ 视神经 Optic
Ⅲ 动眼神经 Oculomotor
Ⅳ 滑车神经 Trochlear
Ⅴ 三叉神经trigeminal
Ⅵ 展神经 (外展神经) Optic abducent
Ⅶ 面神经 Facial
Ⅷ 前庭蜗神经 Vestibular
Ⅸ 舌咽神经glossopharyngeal
Ⅹ 迷走神经 vagus
Ⅺ 副神经 oculomotor facial accessory
Ⅻ 舌下神 经 hypoglossal
口诀: Ⅰ嗅、Ⅱ视、 Ⅲ 动眼, Ⅶ 面、Ⅷ听、 Ⅸ舌咽, Ⅳ 滑、Ⅴ叉 、 Ⅵ外展, 迷、副、舌下顺序全。
– 31对脊神经
感觉神经 运动神经
– 31 pairs of spinal nerves
Sensory nerves Motor nerves
脊神经
12 Cranial Nerves
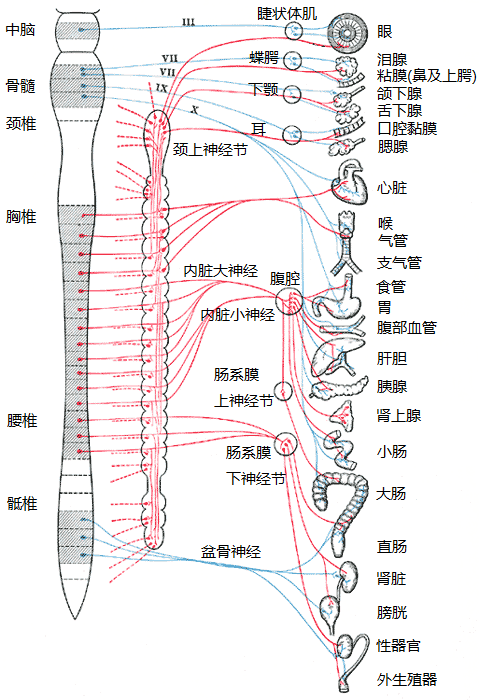
躯体神经系统(SNS) - 控制骨骼肌,受意志控制
自主神经系统(ANS) - 控制不自主的平滑肌和腺体,不受意志直接控制
Somatic nervous system (SNS) - controls skeletal muscles, under voluntary control
Autonomic nervous system (ANS) - controls involuntary smooth muscles and glands, not under direct voluntary control
自主神经系统(ANS) - 也称为植物 性神经。内脏 运动神经是控制和调节动植物共有物质代谢活动,
交感神经 - 副交感神经
Sympathetic nerve - Parasympathetic nerve
(一)交感神经 sympathetic nerve 低级中枢:脊髓T1—L3侧角 周围部 交感干 交感神经节 神经节分支 神经丛 交感部
(I) Sympathetic nerve sympathetic nerve Lower center: lateral angle of spinal cord T1-L3
(二)副交感神经 parasympathetic nerve
(1)低级中枢 脑干副交感神经核
1) Lower center Brainstem
(2)脊髓骶部:脊髓骶2—4节段 的骶副交感核
2) Sacral spinal cord: sacral parasympathetic nuclei in sacral segments 2-4
Cardiovascular System--心血管系统 (循环系统)
• Heart---- 心脏 • Blood----血液 • The Blood Vessels---- 血管
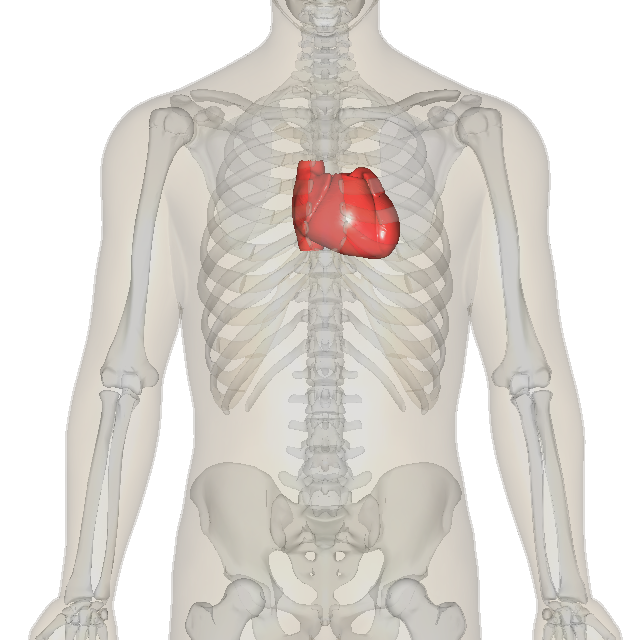
心的体表投影:
Surface projection of the heart:
心脏位置 ⮚胸腔中纵膈内(相当于第2-6 肋软骨或5-8胸椎之间的范围)。 ⮚2/3位于身体正中线的左侧, 1/3在右侧。 1/3 2/3 心脏位置 ⮚长轴:右后上—左前下 ⮚长轴与持笔方向一致 ⮚心尖搏动左侧第五肋间隙锁骨 中线内侧1~2cm。 心脏大小 ⮚本人拳头大小 ⮚心胸比例45-50%
Heart position ⮚Inside the mediastinum in the thoracic cavity (equivalent to the range between the 2nd-6th costal cartilages or the 5th-8th thoracic vertebrae). ⮚2/3 is located on the left side of the midline of the body, and 1/3 is on the right side. 1/3 2/3 Heart position ⮚Long axis: right posterior upper-left anterior lower ⮚Long axis is consistent with the direction of holding the pen ⮚The apex beats on the left side of the fifth intercostal space, 1~2cm inside the midline of the clavicle. Heart size ⮚The size of my fist ⮚Heart-chest ratio 45-50%
心包 是包裹在心和出入心的大血管根部的膜性结构 心包pericardium 纤维心包 浆膜心包
Pericardium is a membranous structure that wraps around the heart and the roots of the large blood vessels entering and leaving the heart Pericardium Fiber pericardium Serous pericardium
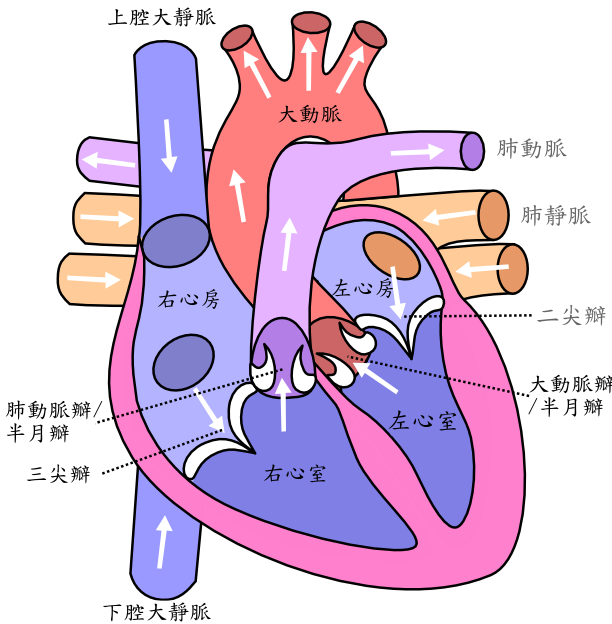
心有四个腔 左心房 左心室 右心房 右心室 左右不通 上下通
The heart has four chambers: left atrium, left ventricle, right atrium, right ventricle.
右心房 right atrium
前部:固有心房
后部:腔静脉窦 上腔静脉口 下腔静脉口
Front: Proper atrium
Back: Vena cava sinus, superior vena cava orifice, inferior vena cava orifice
右心室 Right ventricle
流入道: (窦部)
流 出 道 : (漏斗部 ) 三尖瓣 肺动脉瓣
Inflow tract: (sinus)
Outflow tract: (infundibulum) Tricuspid valve Pulmonary valve
左心房 left atrium
前部 : 固有心房
后部: 左心房窦 四个肺静脉入口 左房室口
Anterior: proper atrium
Posterior: left atrial sinus, four pulmonary vein entrances, left atrioventricular orifice
左心室 left ventricle 分两部(以二尖瓣前瓣为界分)
流入道:二尖瓣
流出道: 主动脉瓣
The left ventricle is divided into two parts (divided by the anterior mitral valve)
Inflow: mitral valve
Outflow: aortic valve
四个心室 :
1. 右心房是一个薄壁腔室,接收来自身体组织的低氧血液。
2. 右心室泵送从右心房接收到的静脉血并将其输送到肺部.
3. 左心房接收从肺部返回的含氧量高的血液.
4. 左心室壁最厚,将含氧血液泵送到身体的各个部位。这 些血液通过动脉,将血液从心脏输送到组织的血管.
Four ventricles:
1. The right atrium is a thin-walled chamber that receives low-oxygen blood from body tissues.
2. The right ventricle pumps venous blood received from the right atrium and delivers it to the lungs.
3. The left atrium receives highly oxygenated blood returning from the lungs.
4. The left ventricle has the thickest walls and pumps oxygenated blood to all parts of the body. This blood passes through arteries, blood vessels that carry blood from the heart to tissues.
四个瓣膜:由于心室是泵室,因此瓣膜都是单向的,位于每个心室 的入口和出口处。
三尖瓣 – 右心室
二尖瓣 – 左心室
肺动脉瓣
主动脉瓣
Four valves: Since the ventricles are pumping chambers, the valves are unidirectional and are located at the entrance and exit of each ventricle.
Tricuspid valve – right ventricle
Mitral valve – left ventricle
Pulmonary valve
Aortic valve
体循环(大循环) 左心室→主动脉及其各级分支→器官内毛细血管→ 右心房
肺循环(小循环) 右心室→ 肺动脉及其各级分支→ 肺泡毛细血管 →肺静脉及其各级属支 →左心房
心的血管 心的血液供应来自左、右冠状动脉
Systemic circulation (large circulation) Left ventricle → aorta and its branches → capillaries in organs → right atrium
Pulmonary circulation (small circulation) Right ventricle → pulmonary artery and its branches → alveolar capillaries → pulmonary vein and its branches → left atrium
Blood vessels of the heart The blood supply of the heart comes from the left and right coronary arteries
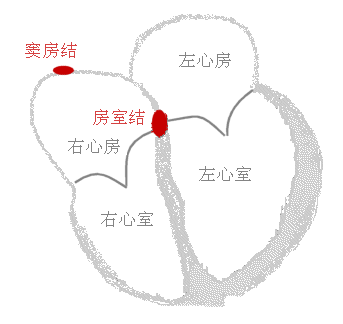
心传导系
(一)窦房结 位置:上腔静脉与右心房交界处 功能: 心的正常起搏点
(二)房室结 位置:房间隔下部右侧心内膜下 功能:将窦房结传来的兴奋发 生短暂延搁再传向心室
(三)房室束(His束) 1、右束支 2、左束支 3、Purkinje 纤维网 房室束、束支和Purkinje 纤维网的功能是将心房传来的兴奋迅速传播 到整个心室的心肌。
Cardiac conduction system
(I) Sinoatrial node Location: Junction of superior vena cava and right atrium Function: Normal pacemaker of the heart
(II) Atrioventricular node Location: Under the right endocardium of the lower part of the atrial septum Function: Delay the excitation from the sinoatrial node briefly and then transmit it to the ventricle
(III) Atrioventricular bundle (His bundle) 1. Right bundle branch 2. Left bundle branch 3. Purkinje fiber network The function of the atrioventricular bundle, bundle branches and Purkinje fiber network is to quickly transmit the excitation from the atrium to the myocardium of the entire ventricle.
淋巴系统
Lymphatic system
• 淋巴器官: 淋巴结 扁桃腺 胸腺 脾
淋巴管 淋巴毛细管 淋巴管 淋巴干 胸导管或右淋巴管
• 胸腺位于心脏上方的胸部上部。 产生一种叫做胸腺素的激素,它有助 于某些白细胞的发育,称为T淋巴细 胞,有助于保护身体免受外来生物的 侵害。 腺体在出生前和生命早期最活跃,在 儿童时期很大,但随着成年期逐渐缩小
• Lymphatic organs: Lymph nodes Tonsils Thymus Spleen
Lymphatic vessels Lymphatic capillaries Lymphatic vessels Lymphatic trunks Thoracic duct or right lymphatic duct
• The thymus gland is located in the upper part of the chest above the heart. It produces a hormone called thymosin, which aids in the development of certain white blood cells, called T lymphocytes, which help protect the body from foreign organisms. The gland is most active before birth and early in life and is large during childhood, but gradually shrinks as we age.
呼吸系统 Respiratory System
鼻 → 咽 → 喉 → (上呼吸道) 气管(下呼吸道) → 各级支气管 → 肺:
主要的气体交换的场所
Nose → pharynx → larynx → (upper respiratory tract) trachea (lower respiratory tract) → bronchi at all levels → lungs:
Main site for gas exchange
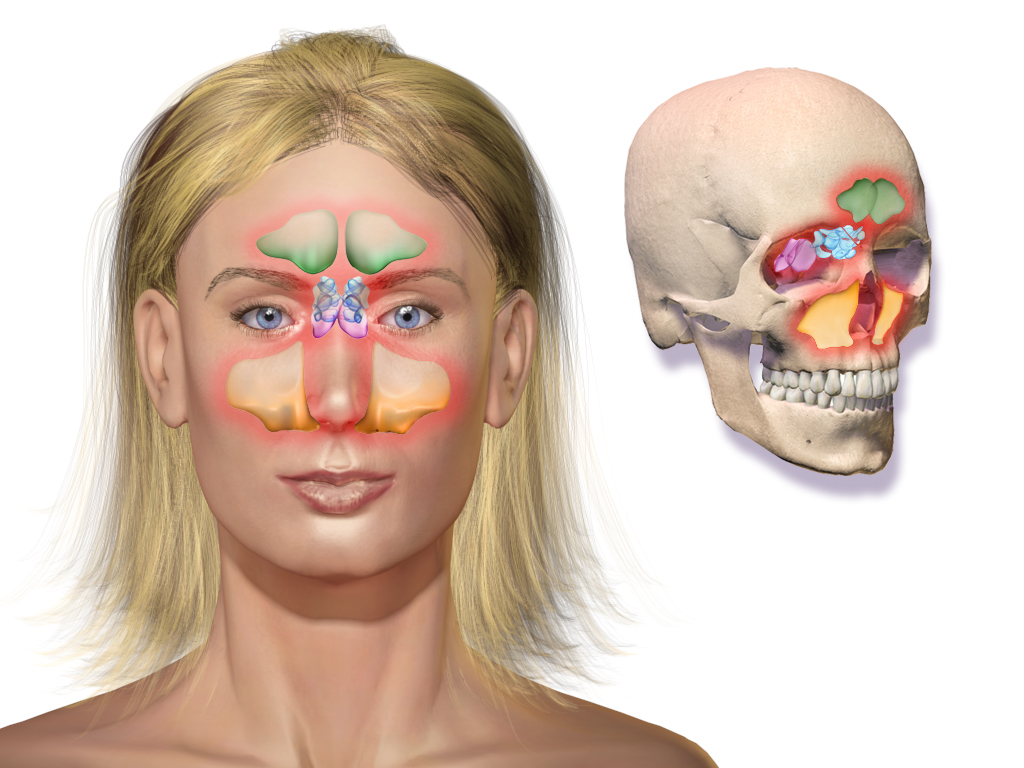
一、鼻 ⎯ 包括外鼻、鼻腔、鼻旁窦
鼻前庭 : 内衬皮肤, 有鼻毛
固有鼻腔 : 内衬黏膜
外鼻:鼻根;鼻背;鼻尖;鼻翼
1. Nose - including external nose, nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses
Nasal vestibule: lined with skin, with nasal hair
Proper nasal cavity: lined with mucosa
External nose: root of nose; dorsum of nose; tip of nose; wing of nose
上壁-筛板:
内侧壁-鼻中隔:
外侧壁 下壁-硬腭 上鼻甲 中鼻甲 下鼻甲
上鼻道 中鼻道 下鼻道 鼻泪管开口
鼻腔:鼻阈 嗅神经
Upper wall - cribriform plate:
Medial wall - nasal septum:
Lateral wall Lower wall - hard palate Superior turbinate Middle turbinate Inferior turbinate
Superior nasal meatus Middle nasal meatus Inferior nasal meatus Nasolacrimal duct opening
Nasal cavity: Nasal threshold Olfactory nerve
鼻旁窦 :额窦 上颌窦 筛窦 蝶窦 ⎯ 鼻腔周围颅骨内的含气腔隙; 内衬黏膜、开口于鼻腔
Paranasal sinuses: frontal sinus maxillary sinus ethmoid sinus sphenoid sinus - air-filled spaces in the skull surrounding the nasal cavity; lined with mucous membrane and opening into the nasal cavity
• 位于鼻腔正后方的上部称为鼻咽部,位于嘴后面的中间部分 称为口咽部, 最低的部分称为喉咽部. 这最后一部分通向喉部, 在前方,通向喉部,食管在后面。
• The upper part just behind the nasal cavity is called the nasopharynx, the middle part behind the mouth is called the oropharynx, and the lowest part is called the laryngopharynx. This last part leads to the larynx, in front, and the esophagus in the back.
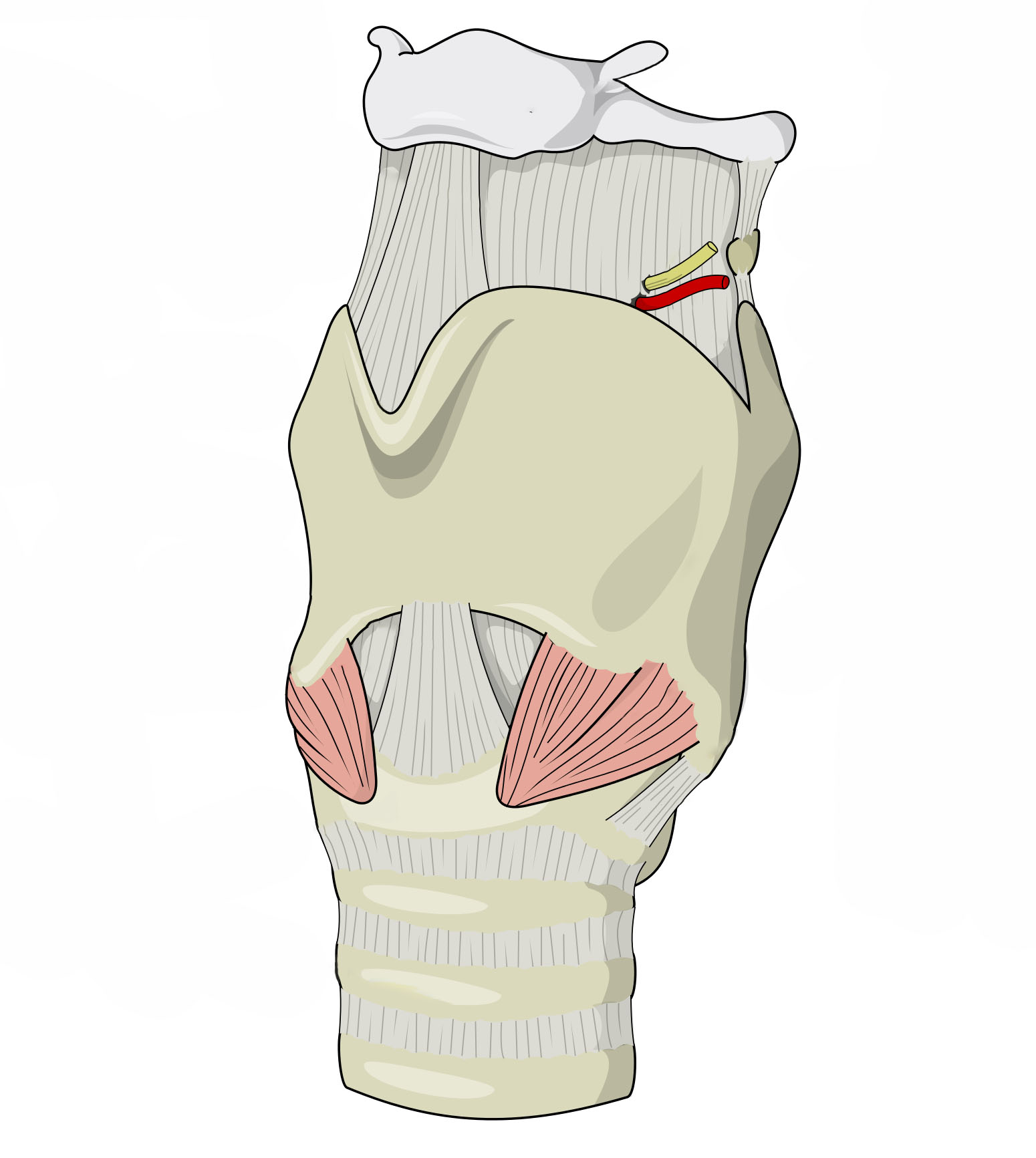
二、喉 (larynx) ⎯ 位于咽和气管之间的一个管道, 既是呼吸道的一部分,又是发音器 官;它由喉软骨连接形成支架, 内外分别覆以喉粘膜喉和喉肌构成 在喉的上端是声带,它们用于产生 语音。 男性的喉部比女性大得多;因此, 喉结在男性中更为突出。喉前端的 软骨主要为甲状软骨
2. Larynx - A tube between the pharynx and the trachea that is both part of the respiratory tract and a vocal organ; it is made up of laryngeal cartilages connected to form a support, covered inside and outside by laryngeal mucosa, larynx and laryngeal muscles. At the top of the larynx are the vocal cords, which are used to produce speech. The male larynx is much larger than the female larynx; therefore, the Adam's apple is more prominent in males. The cartilage at the front of the larynx is mainly the thyroid cartilage.
三、气管、支气管、肺
气管 trachea 气管是一根从喉部下缘延 伸到心脏上方的胸部的管 子。■ 它有一个软骨框架来保持 它的开放。这些软骨的形 状有点像小马蹄铁或字母 C,整个气管都包含着软骨。
左主支气管: 细长、较倾斜 右主支气管: 粗短、较陡直
肺内支气管和支气管肺段 每一肺段支气管及其所分布的肺组织 构成一结构和功能相对独立的单位,称之 为支气管肺段。
3. Trachea, bronchi, and lungs
Trachea The trachea is a tube that extends from the lower edge of the larynx to the chest above the heart. ■ It has a cartilage frame to keep it open. The shape of these cartilages is a bit like a small horseshoe or the letter C, and the entire trachea contains cartilage.
Left main bronchus: slender and relatively inclined Right main bronchus: thick and short, relatively steep
Intrapulmonary bronchi and bronchopulmonary segments Each segment of the bronchus and the lung tissue distributed in it constitute a relatively independent unit in structure and function, called a bronchopulmonary segment.
肺 lung 肺尖; 肺底 肋面; 内侧面: 肺门
左肺: 左肺心切迹; 上叶 下叶
右肺: 斜裂+水平裂 ⎯ 上、中、下叶
lung lung apex; lung base rib surface; medial surface: hilum
left lung: left cardiac notch; upper lobe lower lobe
right lung: oblique fissure + horizontal fissure ⎯ upper, middle and lower lobes
• 支气管越来越小,软骨量越来越少。 • 在细支气管中根本没有软骨;剩下的大部分是 平滑肌,由自主神经系统控制。 在支气管树的每个最小分支的末端,称为 末端细支气管,是一簇气囊,类似于一串 葡萄。这些囊被称为肺泡。
• The bronchi get smaller and smaller, with less and less cartilage. • In the bronchioles there is no cartilage at all; what remains is mostly smooth muscle, controlled by the autonomic nervous system. At the end of each of the smallest branches of the bronchial tree, called the terminal bronchioles, is a cluster of air sacs that resemble a bunch of grapes. These sacs are called alveoli.
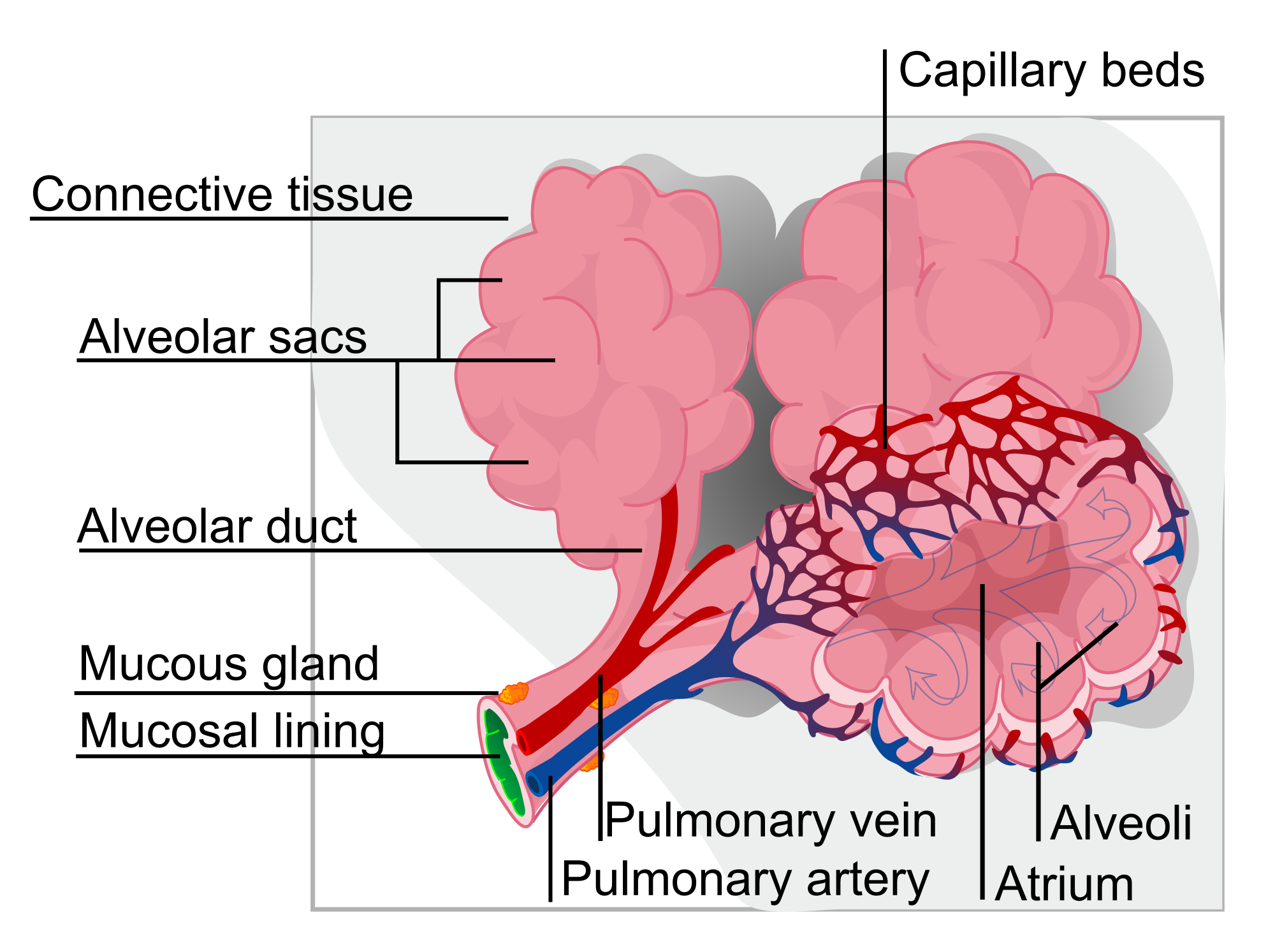
每个肺泡是一个单细胞层。当血液循环通 过肺泡的数百万个微小毛细血管时,这个 非常薄的壁为进入和离开血液的气体提供 了方便的通道。
Each alveolus is a single cell layer. This very thin wall provides an easy passage for gases to enter and leave the blood as blood circulates through the millions of tiny capillaries in the alveoli.
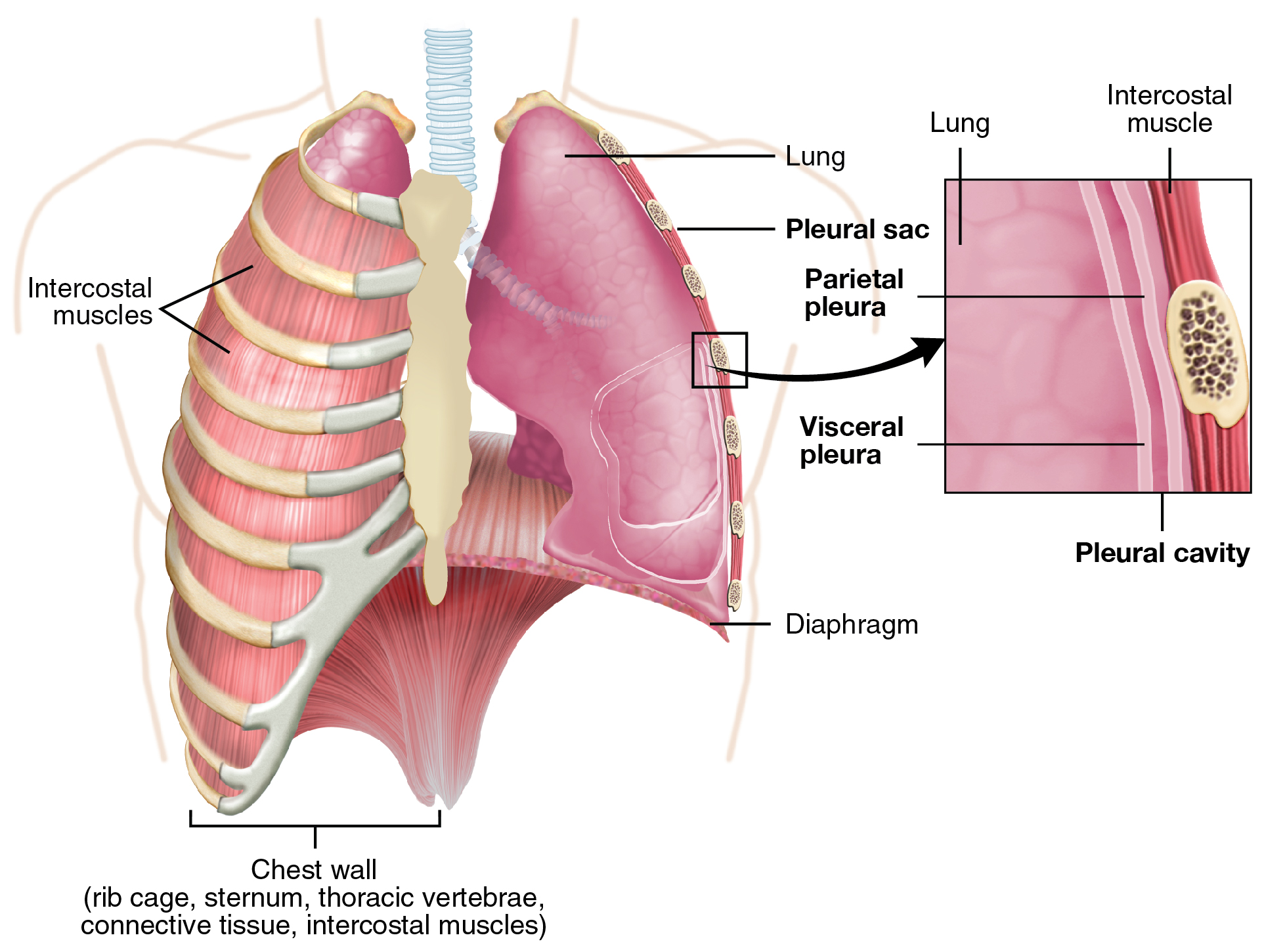
四、胸膜:脏层,壁层,其中是负压空腔
4. Pleura: visceral layer, parietal layer, and negative pressure cavity
五、纵隔 ⎯ 位于胸腔中部的所有 器官和结缔组织的总称; 它 将胸腔分为左、右两部分
纵隔 mediastinum: 胸腺、心、心包 进出心的大血管 气管、食管、胸导管
5. Mediastinum - the general term for all organs and connective tissues located in the middle of the chest cavity; it divides the chest cavity into left and right parts
Mediastinum: thymus, heart, pericardium, large blood vessels in and out of the heart, trachea, esophagus, thoracic duct
消化系统 Digestive System
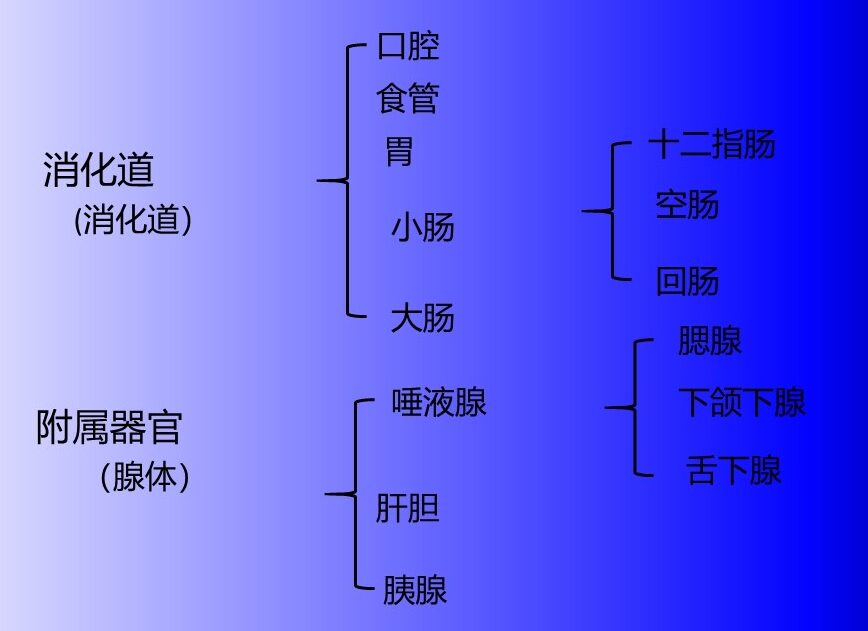
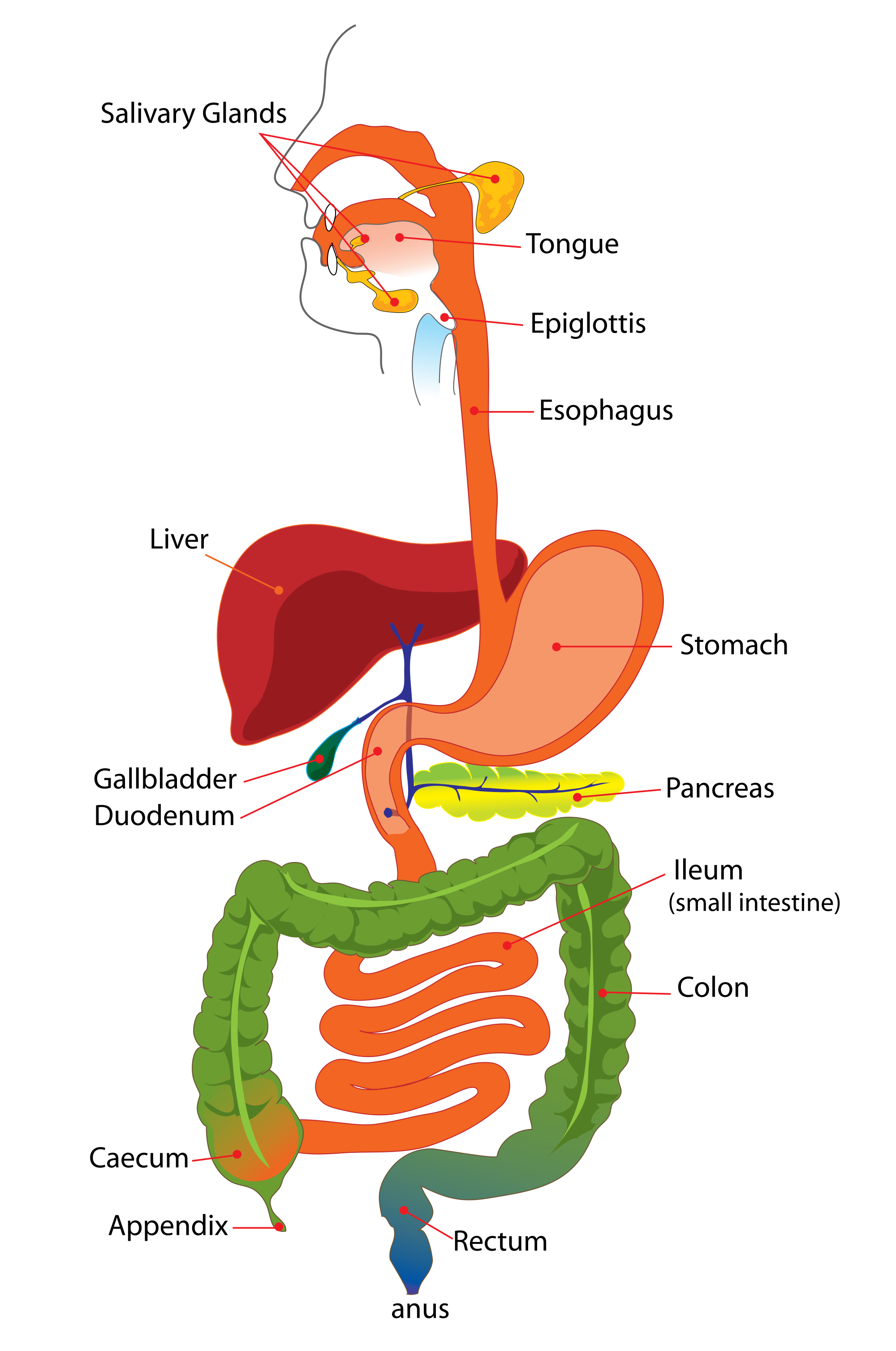
消化道,一条连续的通道,从口腔开始,食物被摄入, 终止于肛门,消化的固体废物被排出体外 辅助器官(消化腺),是消化过程所必需的,但不是消化 道的直接部分。它们通过管道将物质释放到消化道中。
Alimentary tract, a continuous passage that begins at the mouth, where food is taken in, and ends at the anus, where solid waste products of digestion are excreted Accessory organs (digestive glands), which are necessary for the digestive process but are not a direct part of the alimentary tract. They release substances into the alimentary tract through tubes.

一、 口腔 (Oral cavity) 口腔以上、下牙弓为界 上唇 下唇 口裂、口角。
口腔的前壁为唇、侧壁为颊、顶为腭、前部为硬腭,后部为软腭,口腔底为黏膜和肌等结构。
1. Oral cavity The oral cavity is bounded by the upper and lower dental arches, upper lip, lower lip, cleft mouth, and corners of mouth.
The front wall of the oral cavity is the lip, the side wall is the cheek, the top is the palate, the front part is the hard palate, the back is the soft palate, and the floor of the oral cavity is composed of mucosa and muscle structures.
二、咽 (pharynx) ⎯ 前后略扁的漏斗形肌性管道,分为鼻咽、 口咽、喉咽三部分,是消化道与呼吸道的共 同通路
■ 咽部通常被称为喉咙。
■ 咽部也向上延伸至鼻腔并向下延伸至喉部水 平。
2. Pharynx - a funnel-shaped muscular tube that is slightly flattened front and back. It is divided into three parts: nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx. It is the common passage for the digestive tract and respiratory tract.
■ The pharynx is usually called the throat.
■ The pharynx also extends upward to the nasal cavity and downward to the level of the larynx.
三、食管 (esophagus) ⎯连接咽与胃的肌性管道,全长约 25-27cm. 分为颈、胸、腹三段 食管的生理狭窄
第一狭窄:与咽的连接处 距中切牙约 15cm
第二狭窄:与左支气管交叉处 距中切牙约 25cm
第三狭窄:经膈的食管裂孔处 距中切牙约 40cm
3. Esophagus - a muscular tube connecting the pharynx and stomach, with a total length of about 25-27cm. It is divided into three sections: cervical, thoracic, and abdominal. Physiological stenosis of the esophagus
First stenosis: the junction with the pharynx is about 15cm away from the central incisor
Second stenosis: the intersection with the left bronchus is about 25cm away from the central incisor
Third stenosis: the esophageal hiatus through the diaphragm is about 40cm away from the central incisor
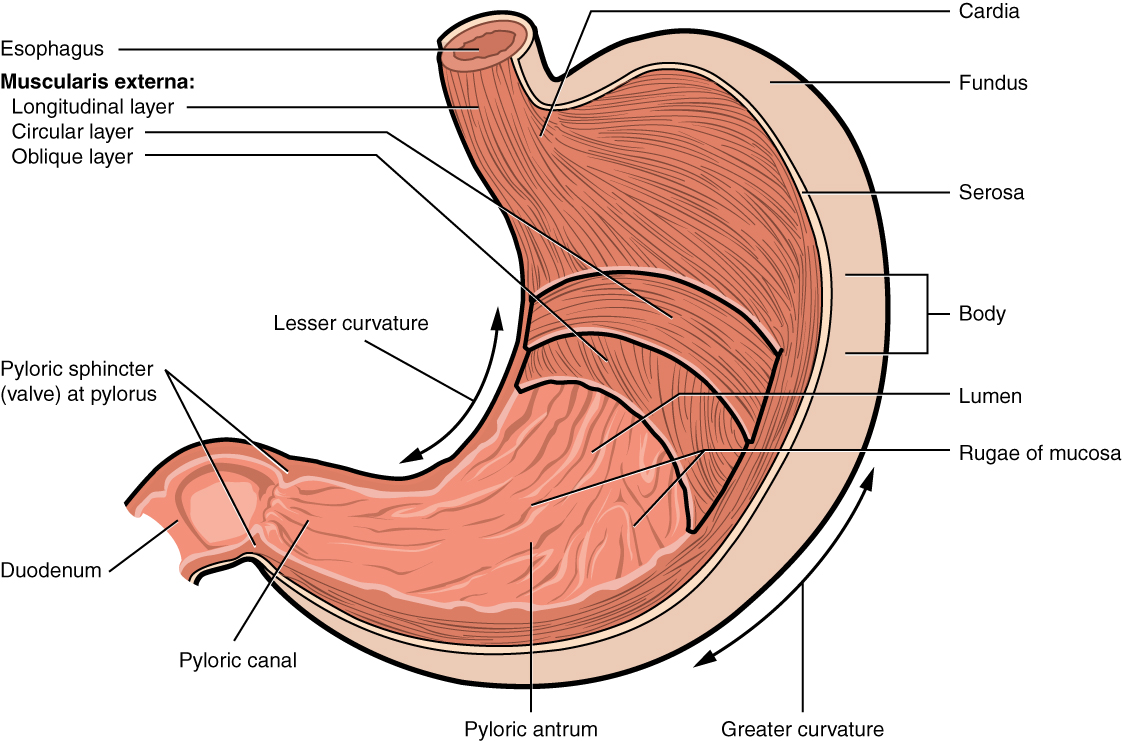
Stomach 胃
四、胃 (Stomach) 分部 贲门部 胃底 胃体 幽门部
4. Stomach Division Cardiac Fundus Body Pyloric
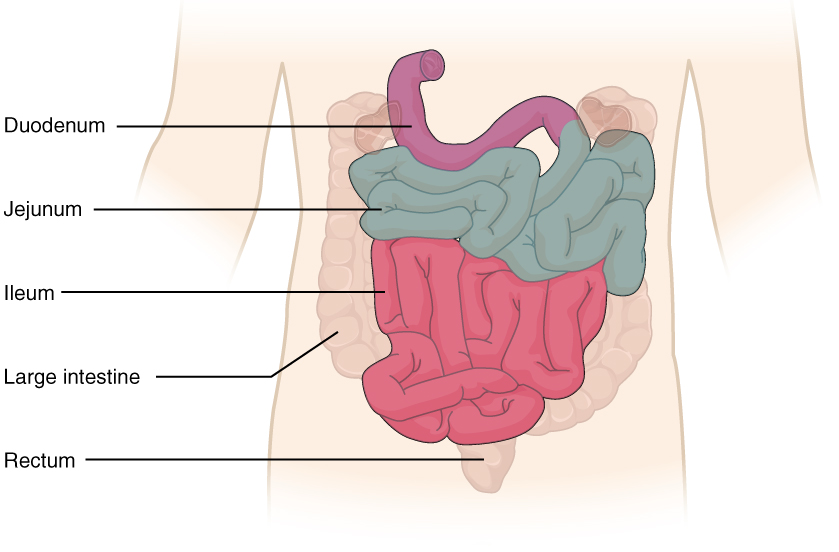
Small_Intestine 小肠
五、小肠 (small intestine) ⎯ 包括十二指肠、空肠、回肠
小肠是消化道最长的部分。它被称为小肠,因为它虽然比大 肠长,但直径更小,平均宽度约为 2.5 厘米。小肠长约 6 m。 小肠的前 25 厘米左右组成十二指肠。
十二指肠(Duodenum) 十二指肠大乳头 ← 胰管,十二指肠小乳头 ← 副胰管
十二指肠之外还有两个部分:空肠,它构成了小肠接下来的 五分之二,位于左上腹。回肠,构成了剩余的部分 (3/5),位于 右下腹。
空肠与回肠为小肠的主体部分,借小肠系膜 悬吊于腹后壁, 空肠与回肠两 者间没有的分界标志
5. Small intestine - includes the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
The small intestine is the longest part of the digestive tract. It is called the small intestine because, although it is longer than the large intestine, it has a smaller diameter, with an average width of about 2.5 cm. The small intestine is about 6 m long. The first 25 cm or so of the small intestine constitutes the duodenum.
Duodenum Duodenum papilla ← pancreatic duct, duodenum papilla ← accessory pancreatic duct
There are two other parts outside the duodenum: the jejunum, which makes up the next two-fifths of the small intestine and is located in the left upper abdomen. The ileum, which makes up the remaining part (3/5), is located in the right lower abdomen.
The jejunum and ileum are the main parts of the small intestine, suspended from the posterior abdominal wall by the small intestinal mesentery, and there is no dividing mark between the jejunum and ileum
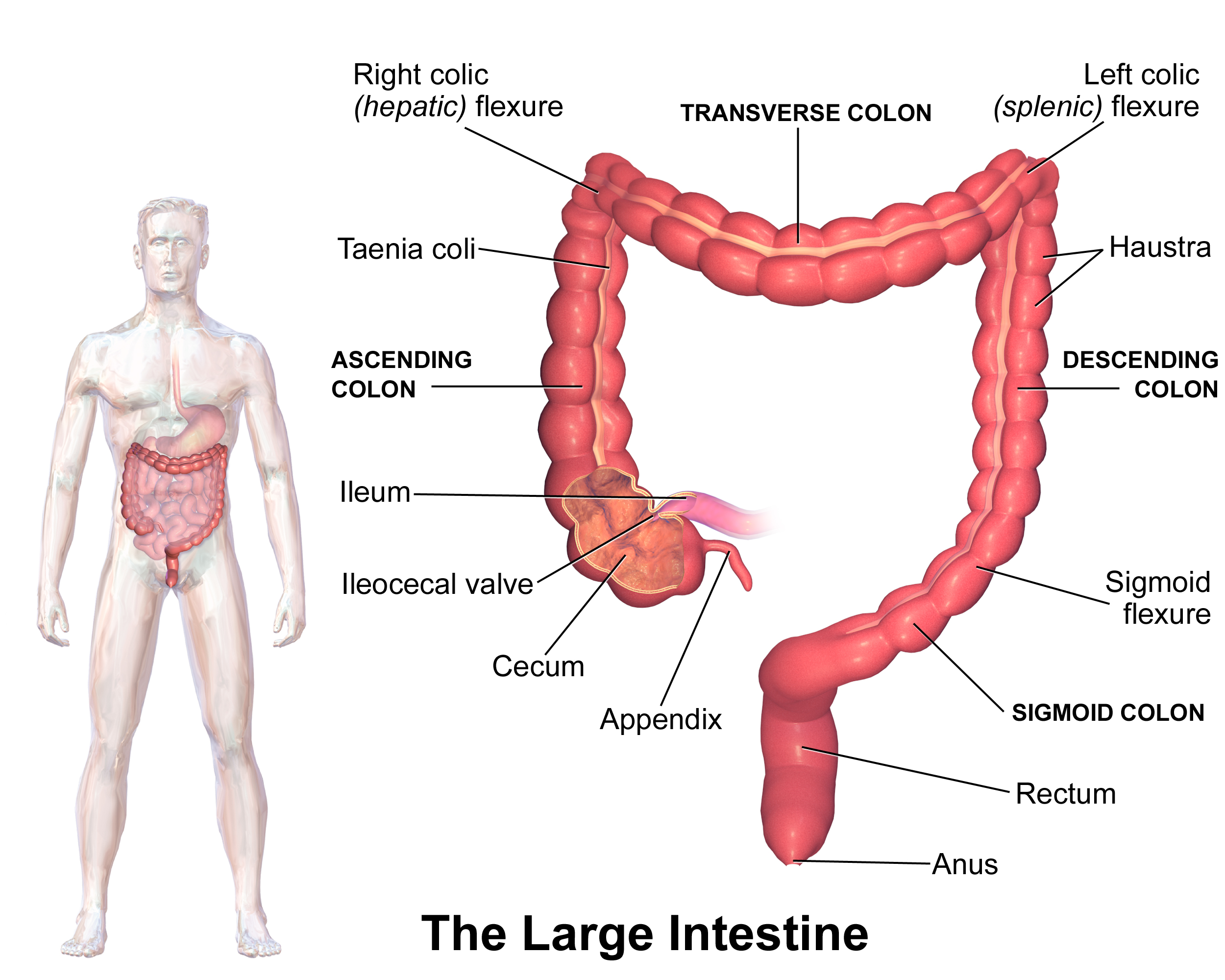
六、大肠 (large intestine) 盲肠 (cecum) 和阑尾 (appendix) 升结肠 横结肠 ⎯ 横结肠系膜 降结肠 乙状结肠 ⎯ 乙状结肠系膜 结肠 (colon) 直肠 (rectum) 肛管 (anal canal)
大肠直径约 6.5 厘米,长约 1.5 米。 大肠开始于腹部的右下区域。
第一部分是一个小袋子,叫做盲肠. 附在盲肠是一个小的盲管,内含淋巴组织;它被称为阑尾,阑尾的形态 蚯蚓状、 一般 5-7cm长 ,该组织因感染而发炎或障 碍是阑尾炎。
第二部分, 为升结肠,向上延伸沿腹部右侧朝向肝脏。然后大肠弯曲穿过腹部,形 成横结肠。此时它急剧弯曲并延伸腹部左侧向下进入骨盆,形成降结肠。 结肠下部弯曲后面呈 S 形并继续向下乙状结肠。远端大肠的狭窄部分是叫做肛管。 末端叫做肛门。
VI. Large Intestine Cecum and Appendix Ascending colon Transverse colon ⎯ transverse colon mesocolon Descending colon Sigmoid colon ⎯ sigmoid colon mesocolon Colon Rectum Anal canal
The large intestine is about 6.5 cm in diameter and about 1.5 m long. The large intestine begins in the lower right area of the abdomen.
The first part is a small bag called the cecum. Attached to the cecum is a small blind tube containing lymphatic tissue; it is called the appendix, which is worm-like in shape and is generally 5-7 cm long. Inflammation or obstruction of this tissue due to infection is appendicitis.
The second part, the ascending colon, extends upward along the right side of the abdomen toward the liver. The large intestine then bends through the abdomen to form the transverse colon. At this point it bends sharply and extends down the left side of the abdomen into the pelvis to form the descending colon. The lower part of the colon bends back into an S shape and continues down the sigmoid colon. The narrow part of the distal large intestine is called the anal canal. The end is called the anus.
消化腺 Digestive glands
Salivary_glands 口腔唾液腺
口腔唾液腺: 腮腺 下颌下腺 舌下腺
腮腺最大,位于耳朵下方和前方。
Oral salivary glands: Parotid gland Submandibular gland Sublingual gland
The parotid gland is the largest and is located below and in front of the ear.
Liver_肝
肝 (liver;hepato-) 位置:主要位于右季肋区和腹上区
体表投影 上缘:于右锁骨中线处平第5肋 右季肋区 ⎯ 与肋弓下缘一致 腹上区 ⎯ 剑突下2-3 cm 下缘 5 th rib 2-3cm
肝脏, 是身体最大的腺体。 它位于膈下腹腔的右上部分。正常大小的肝 脏下缘与肋骨下缘齐平。 人的肝脏和超市里看到的动物肝脏是一样的 红棕色。它有一个大的右叶和一个较小的左 叶。
肝脏通过两条血管供血:门静脉和肝动脉。
Liver (liver; hepato-) Location: mainly located in the right hypochondrium and epigastric region
Body surface projection Upper edge: at the level of the 5th rib at the right midclavicular line Right hypochondrium ⎯ in line with the lower edge of the costal arch Epigastric region ⎯ 2-3 cm below the xiphoid process Lower edge 5th rib 2-3cm
The liver is the largest gland in the body. It is located in the upper right part of the abdominal cavity below the diaphragm. The lower edge of a normal-sized liver is flush with the lower edge of the ribs. The human liver is the same reddish-brown color as the animal livers you see in supermarkets. It has a large right lobe and a smaller left lobe.
The liver is supplied with blood through two blood vessels: the portal vein and the hepatic artery.
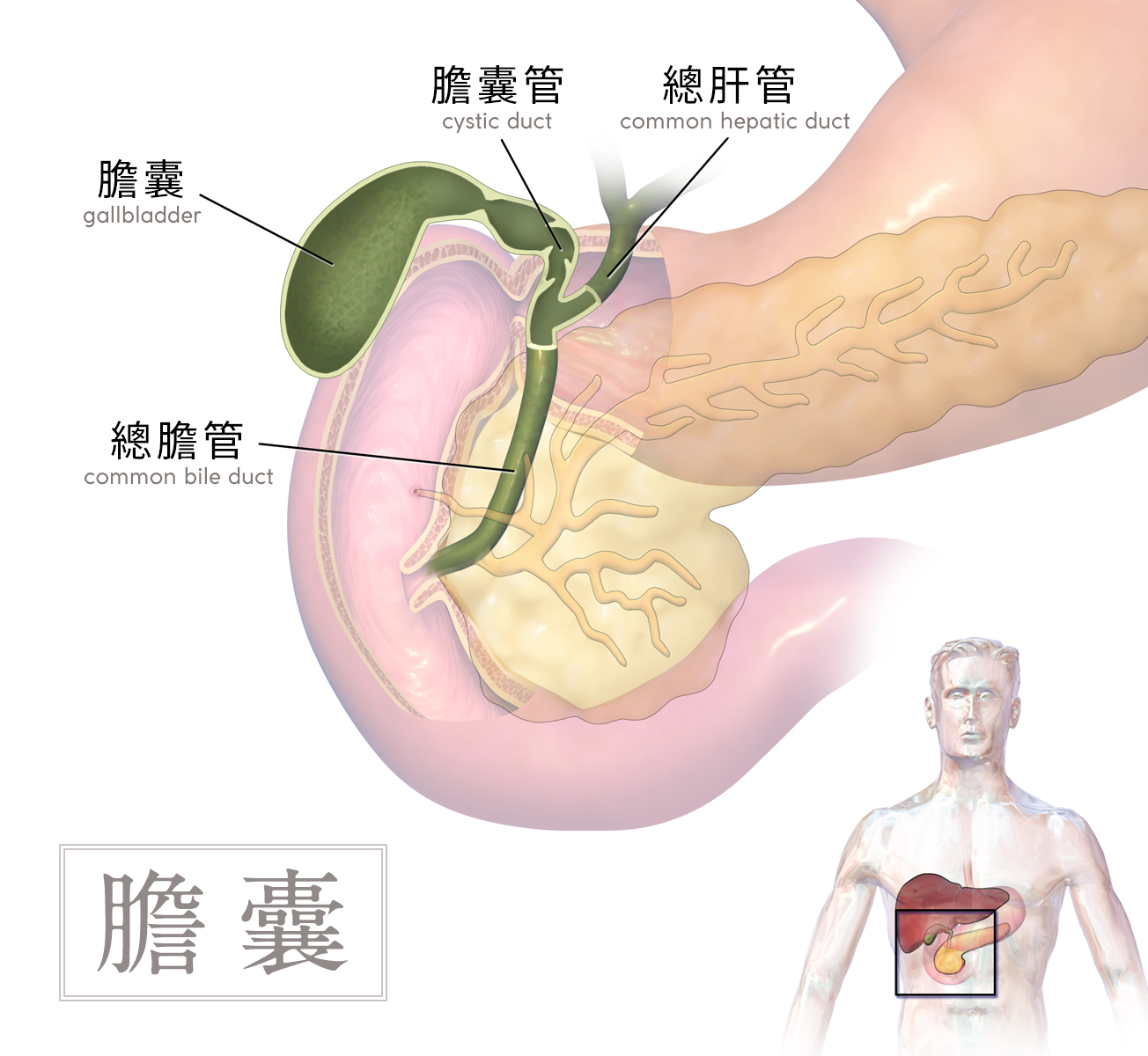
胆囊位于肝脏的下面
胆囊:呈倒梨形 胆囊底 胆囊体 胆囊颈
肝外胆道 Extrahepatic bile ducts 构 成 胆囊 胆囊管 胆总管
The gallbladder is located below the liver
Gallbladder: inverted pear-shaped Gallbladder fundus Gallbladder body Gallbladder neck
Extrahepatic bile ducts Extrahepatic bile ducts Composition Gallbladder Cystic duct Common bile duct
胰 Pancreas 位置:横行于第1-2腰椎前方, 胃的后方
胰头,胰体, 胰尾
胰管:行于胰实质内,与其 长轴平行
Pancreas Location: running horizontally in front of the 1st and 2nd lumbar vertebrae, behind the stomach
Head, body and tail of the pancreas
Pancreatic duct: running in the pancreatic parenchyma, parallel to its long axis
消化道的壁
• 从食道到肛门的消化道壁在整 个结构上都相似。 • 黏膜 • 粘膜下层 • 平滑肌 • 浆膜这是一部分腹膜。
The wall of the digestive tract
• The wall of the digestive tract from the esophagus to the anus is similar throughout its structure. • Mucosa • Submucosa • Smooth muscle • Serosa This is part of the peritoneum.
Peritoneum 覆膜
腹膜 • 腹腔内衬有一层薄而有光泽 的浆膜,也覆盖了大部分腹 部。
• 这种膜排列在腹部的部分称 为壁层腹膜;覆盖器官被称 为内脏腹膜。
• 肠系膜是腹膜的双层部分, 呈扇形。把手部分附在后壁 上,膨胀的长边附在小肠上。
• 从结肠延伸到后壁的腹膜部 分是结肠系膜.
网膜
• 大网膜 含有大量脂肪的大双层腹膜像围裙一样悬挂在肠 道前部。从胃的下缘延伸到腹部的骨盆部分,然后循环回到横结肠。
• 小网膜 在胃和肝脏之间延伸
Peritoneum • The abdominal cavity is lined with a thin, shiny layer of serous membrane that also covers much of the abdomen.
• The portion of this membrane that lines the abdomen is called the parietal peritoneum; the portion that covers the organs is called the visceral peritoneum.
• The mesentery is a double-layered portion of the peritoneum that is fan-shaped. The knob portion is attached to the back wall, and the long, inflated side is attached to the small intestine.
• The portion of the peritoneum that extends from the colon to the back wall is the mesocolon.
Omentum
• Greater Omentum A large double-layered membrane containing a lot of fat that hangs like an apron over the front of the intestine. It extends from the lower edge of the stomach to the pelvic portion of the abdomen and then loops back to the transverse colon.
• Lesser Omentum Extends between the stomach and liver
泌尿系统
Urinary system
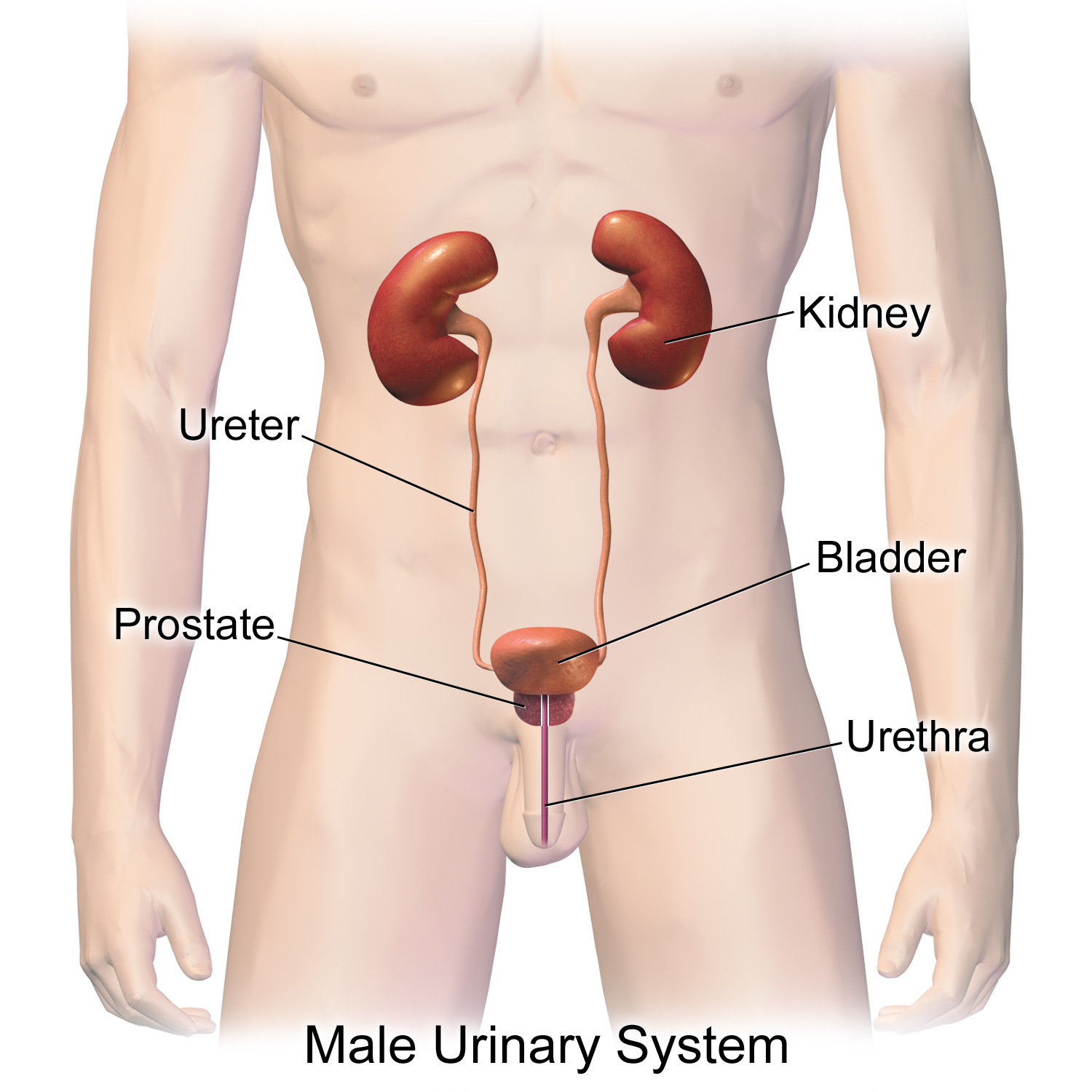
泌尿系统的组成
肾 kidney 实质性器官,左右各一,位于腹后壁脊柱两侧 形似蚕豆。
新鲜肾呈红褐色 上端:宽而薄 下端:窄而厚 前面:凸向前外 后面:平坦,紧贴腹后壁 外缘:突向外 内缘:中凹,有肾门、肾窦、肾蒂
Composition of the urinary system
Kidney is a solid organ, one on each side, located on both sides of the spine on the posterior abdominal wall. It is shaped like a broad bean.
Fresh kidneys are reddish brown. Upper end: wide and thin Lower end: narrow and thick Front: convex to the front and outside Back: flat, close to the posterior abdominal wall Outer edge: protruding outward Inner edge: concave in the middle, with renal hilum, renal sinus, and renal pedicle.
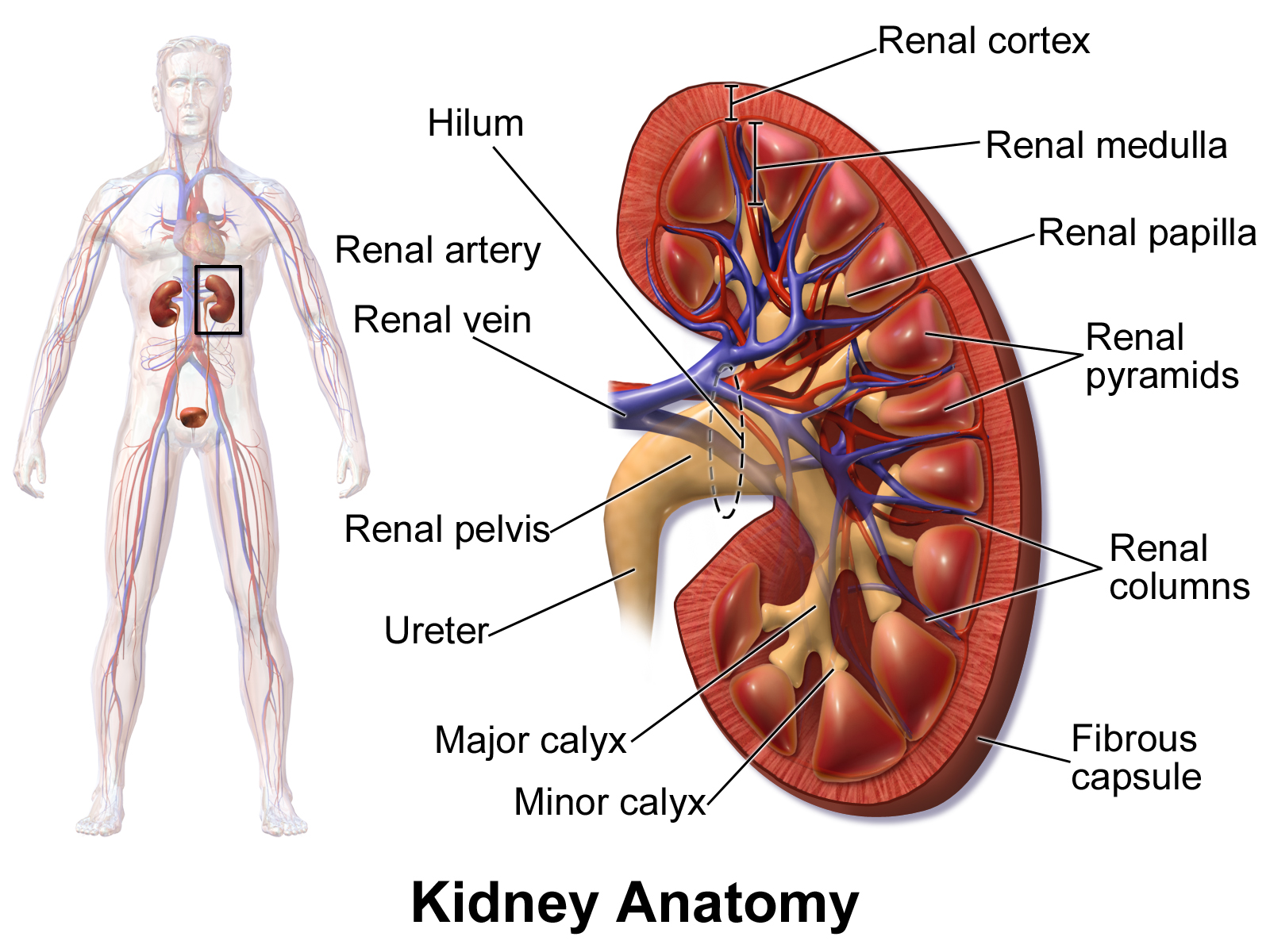
肾的结构
肾门:肾内侧缘 中部凹陷,称为 肾门,肾神经、 血管、淋巴管、 肾盂等出入部位
肾窦: 肾门向肾内凹陷 形成的较大的腔隙,其内 容纳肾小盏、肾大盏、肾 盂、肾A分支、肾V属支 及神经、淋巴管、脂肪等
肾蒂:出入肾门的 结构被结缔组织包 裹在一起形成
肾的位置 位于腹腔后上部,腰部脊柱两旁
左肾:T11下缘~L2下缘
右肾:比左肾低半个椎体
肾门:L1椎体平面,相当于第9肋软骨前端高度,在正中线外侧约5cm
肾区(脊肋角):竖脊肌的外侧缘与第12肋之间的区域
Structure of kidney
Hilum: The middle part of the inner edge of the kidney is concave, called the hilum, where the renal nerves, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, renal pelvis, etc. enter and exit
Renal sinus: The hilum is concave into the kidney to form a larger cavity, which contains the renal calyx, renal calyx, renal pelvis, renal A branch, renal V branch, nerves, lymphatic vessels, fat, etc.
Renal pedicle: The structure entering and exiting the hilum is wrapped together by connective tissue
The location of the kidney is located in the upper back of the abdominal cavity, on both sides of the lumbar spine
Left kidney: T11 lower edge ~ L2 lower edge
Right kidney: half a vertebra lower than the left kidney
Hilum: L1 vertebral plane, equivalent to the height of the front end of the 9th costal cartilage, about 5cm outside the midline
Renal area (costo-spinal angle): the area between the outer edge of the erector spinae and the 12th rib
肾的毗邻
左肾: 上部接肾上腺 前上部与胃底后面相邻 中部与胰尾和脾血管相接触 下部邻接空肠和结肠左曲
右肾: 上部接肾上腺 前上部与肝相邻 下部与结肠右曲相接触 内侧缘邻接十二指肠降部
两肾后面: 上1/3与膈相邻, 在12肋与竖脊肌外侧缘之间 的区域 在临床上称为肾区
肾的被膜 纤维囊 包于肾实质表面的薄层结缔组织膜,由致密结缔组织和弹性纤维构成 肾门处,此膜分为两层,一层贴于组织膜外面,另-层包被肾窦内结构表面 纤维囊与组织膜连结疏松,易于剥离
肾脂肪囊 ,是位于纤维囊外周、包裹肾脏的 脂肪层。肾的边缘部脂肪丰富,并经肾门进入肾窦
肾筋膜 位于脂肪囊的外面,包被肾上腺和肾的周围, 有固定肾脏和维持肾的正常位置的功能。
Neighboring kidneys
Left kidney: The upper part is connected to the adrenal gland, the upper and anterior parts are adjacent to the back of the gastric fundus, the middle part is in contact with the pancreatic tail and splenic vessels, and the lower part is adjacent to the jejunum and the left flexure of the colon
Right kidney: The upper part is connected to the adrenal gland, the upper and anterior parts are adjacent to the liver, the lower part is in contact with the right flexure of the colon, and the inner edge is adjacent to the descending part of the duodenum
Behind both kidneys: The upper 1/3 is adjacent to the diaphragm, and the area between the 12th rib and the outer edge of the erector spinae is clinically called the renal area
Renal capsule Fiber capsule is a thin layer of connective tissue membrane wrapped around the surface of the renal parenchyma, composed of dense connective tissue and elastic fibers. At the renal hilum, this membrane is divided into two layers, one layer is attached to the outside of the tissue membrane, and the other layer covers the surface of the internal structure of the renal sinus. The fiber capsule is loosely connected to the tissue membrane and is easy to peel off
Renal fat capsule is a fat layer located outside the fiber capsule and wraps the kidney. The kidney has abundant fat on the edge, and enters the renal sinus through the renal hilum
The renal fascia is located outside the fat capsule, wrapping around the adrenal gland and kidney, and has the function of fixing the kidney and maintaining the normal position of the kidney.
肾实质
肾皮质:
厚约1--1.5cm,约占肾实质厚度的1/3。新鲜标本为红褐色, 富含血管并可见许多红色点状细小颗 粒,由肾小体与肾小管组成。
肾髓质:
约占肾实质厚度的2/3 肾锥体可见15~20个呈圆锥形、底朝皮质、尖向肾窦、光 泽致密、有许多颜色较深放射状条纹的。肾锥体的条纹由 肾直小管和血管平行排列形成 2-3个肾锥体尖端合并成肾乳头,并突入呈漏斗形的肾小盏内,肾乳头顶端有许多小孔称乳头孔
Renal parenchyma
Renal cortex:
About 1-1.5cm thick, accounting for about 1/3 of the thickness of the renal parenchyma. Fresh specimens are reddish brown, rich in blood vessels and many red dot-like small particles can be seen, composed of renal corpuscles and renal tubules.
Renal medulla:
About 2/3 of the thickness of the renal parenchyma 15 to 20 renal pyramids can be seen, which are conical, with the base facing the cortex and the tip facing the renal sinus, shiny and dense, and have many darker radial stripes. The stripes of the renal pyramids are formed by the parallel arrangement of the renal straight tubules and blood vessels. The tips of 2-3 renal pyramids merge into renal papillae and protrude into the funnel-shaped renal calyx. There are many small holes on the top of the renal papillae, called papillary holes.
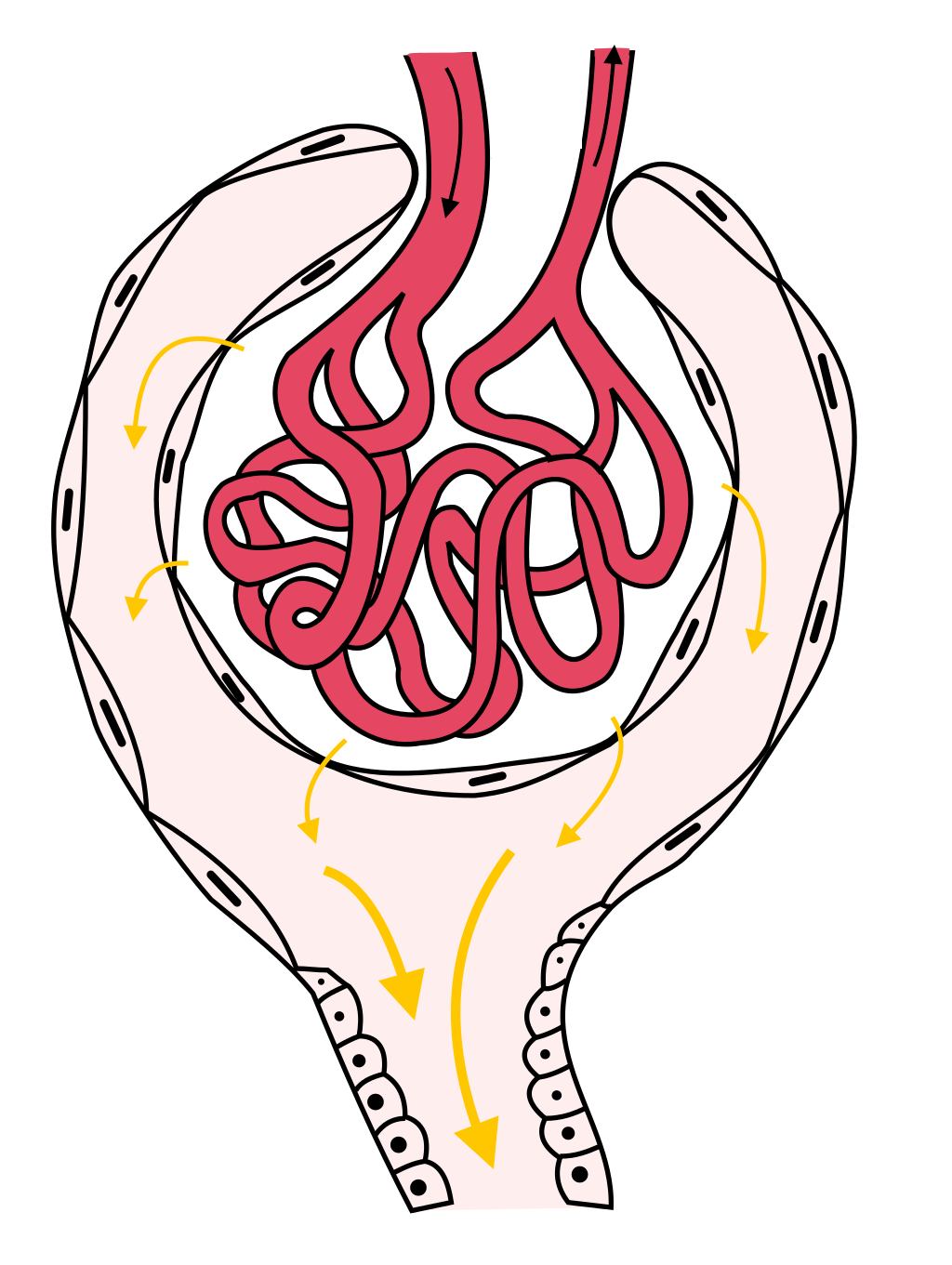
肾的组织学结构 肾单位 (形成尿液)
Histological structure of kidney Nephron (urine forming)
血管球 + 肾小囊 = 肾小体
肾小球(血管球):入球小动脉反复分支形 成盘曲的毛细血管袢
肾小囊:膨大的双层囊性结构,包绕在肾小球周围, 是肾小管的起始部
血管球 + 肾小囊 = 肾小体 + 肾小管 = 肾单位
肾 小 管:近端小管 和髓袢降支粗段 髓袢降支细段和髓袢升支细段 髓袢升支粗段和远曲小管
肾小管内的液体流经肾小管各段后进入集合管,开口于肾乳头。肾产生的终尿经乳头孔流入肾小盏→肾大盏→肾盂
2-3个肾小盏合成一 个肾大盏,再由2~3个肾大盏汇合形成一个肾盂 肾盂离开肾门向下弯行,约在T2椎体上缘水平,逐渐变细 移行为输尿管,成人肾盂容积约7.5ml
Glomerulus + renal capsule = renal body
Glomerulus (glomerulus): afferent arterioles branch repeatedly to form winding capillary loops
Renal capsule: an enlarged double-layer cystic structure that surrounds the glomerulus and is the starting point of the renal tubule
Glomerulus + renal capsule = renal body + renal tubule = nephron
Renal tubule: proximal tubule and thick segment of descending limb of loop of Henle, thin segment of descending limb of loop of Henle and thin segment of ascending limb of loop of Henle, thick segment of ascending limb of loop of Henle and distal convoluted tubule
The fluid in the renal tubule flows through each segment of the renal tubule and enters the collecting duct, opening at the renal papilla. The final urine produced by the kidney flows into the renal calyx through the papillary foramen → renal calyx → renal pelvis
2-3 renal calyxes merge into a renal calyx, and then 2-3 renal calyxes merge to form a renal pelvis. The renal pelvis bends downward from the renal hilum and gradually becomes thinner at the level of the upper edge of the T2 vertebral body. It migrates to the ureter. The volume of the renal pelvis in an adult is about 7.5ml
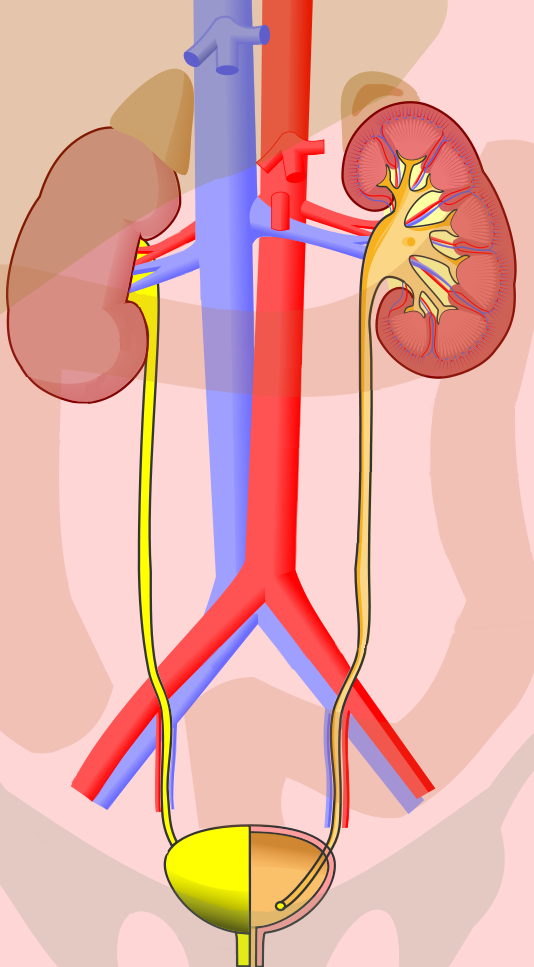
Ureter_输尿管
输尿管 Ureter 一对细长的肌性管道(平滑肌),起于肾盂止于膀胱 长约20-30cm,管径0.5-1cm(最窄处0.2-0.3cm)
输尿管的三个狭窄
①上狭窄 , 位于肾盂输尿管移行处
②中狭窄 ,位于骨盆上口,输尿管跨过髂血管处
③下狭窄 在输尿管的壁内部
Ureter A pair of slender muscular tubes (smooth muscle) that start from the renal pelvis and end at the bladder. They are about 20-30cm long and 0.5-1cm in diameter (0.2-0.3cm at the narrowest point).
Three strictures of the ureter
① Upper stricture, located at the transition between the renal pelvis and ureter
② Middle stricture, located at the upper opening of the pelvis, where the ureter crosses the iliac vessels
③ Lower stricture, inside the wall of the ureter
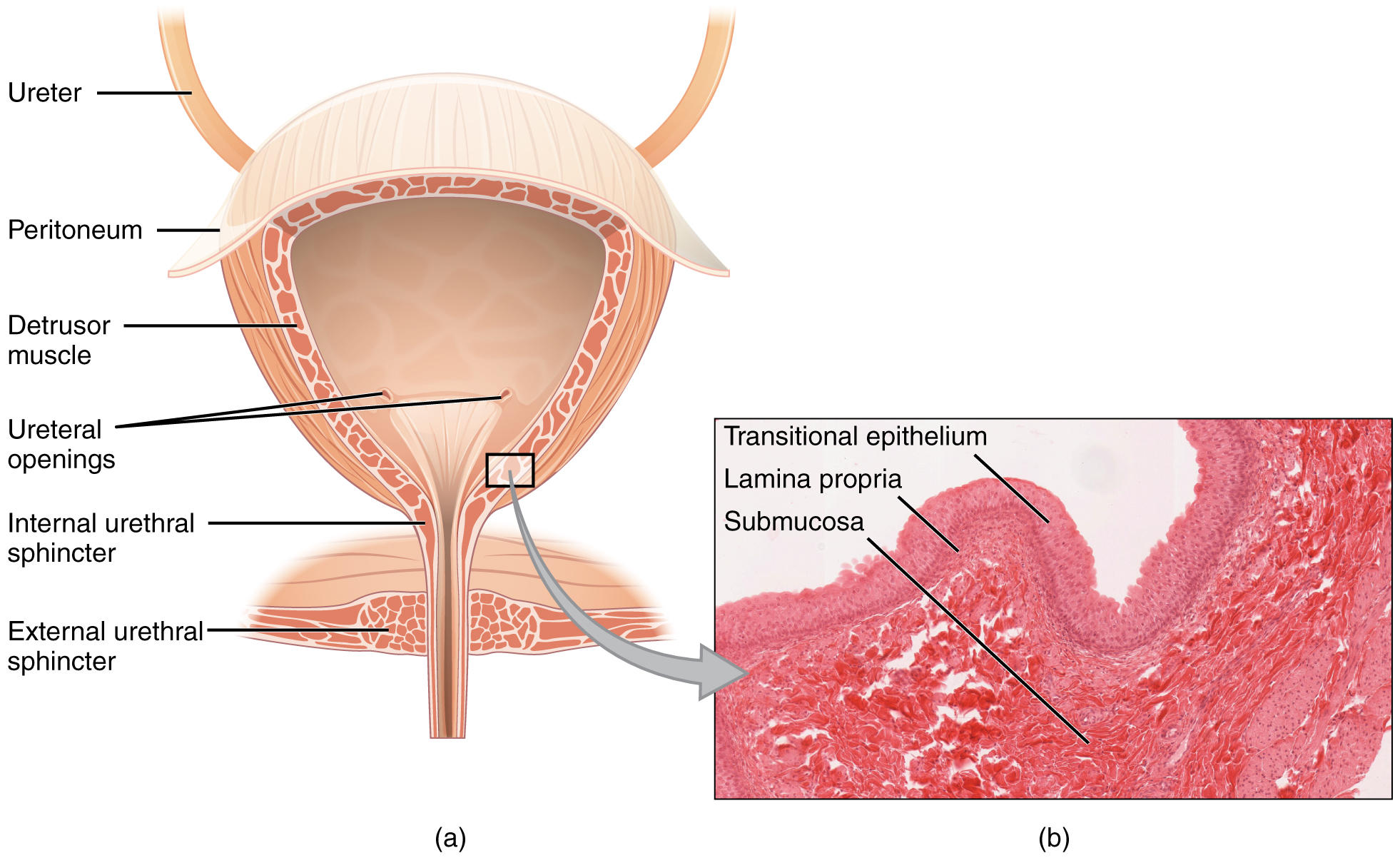
膀胱 Bladder ◆肌性囊状器官(平滑肌)
◆形状、大小和壁的厚度随尿液充盈程度而异
◆贮存尿液
膀胱容量 ◆正常成人350-500ml ◆最大容量800ml ◆新生儿膀胱容量为成人的1/10
◆女性的容量小于男性,老年人因膀胱肌张力低而容量增大
膀胱的位置与毗邻(男性)
◆正常位于盆腔前部,耻骨联合后方 ◆空虚时位于盆腔内,充盈时超过耻骨联合
前方:耻骨联合 下方:前列腺 后方:输精管壶腹、精囊、直肠
膀胱的位置与毗邻(女性)
◆正常位于盆腔前部,耻骨联合后方 ◆空虚时位于盆腔内,充盈时超过耻骨联合
前方:耻骨联合 下方:尿生殖膈 后上方:子宫 女性怀孕期间,子宫体积增大,引起尿频
Bladder ◆Muscular sac-like organ (smooth muscle)
◆The shape, size and wall thickness vary with the degree of urine filling
◆Store urine
Bladder capacity ◆Normal adult 350-500ml ◆Maximum capacity 800ml ◆Newborn bladder capacity is 1/10 of adult
◆Female capacity is smaller than male capacity, and the elderly have increased capacity due to low bladder muscle tension
Location and adjacent areas of the bladder (male)
◆Normal location in the front of the pelvic cavity, behind the pubic symphysis ◆Located in the pelvic cavity when empty, and exceeds the pubic symphysis when full
Anterior: pubic symphysis Below: prostate Back: ampulla of vas deferens, seminal vesicle, rectum
Location and adjacent areas of the bladder (female)
◆Normal location in the front of the pelvic cavity, behind the pubic symphysis ◆Located in the pelvic cavity when empty, and exceeds the pubic symphysis when full
Anterior: pubic symphysis Below: urogenital diaphragm Back and top: uterus During pregnancy, the uterus increases in size, causing frequent urination
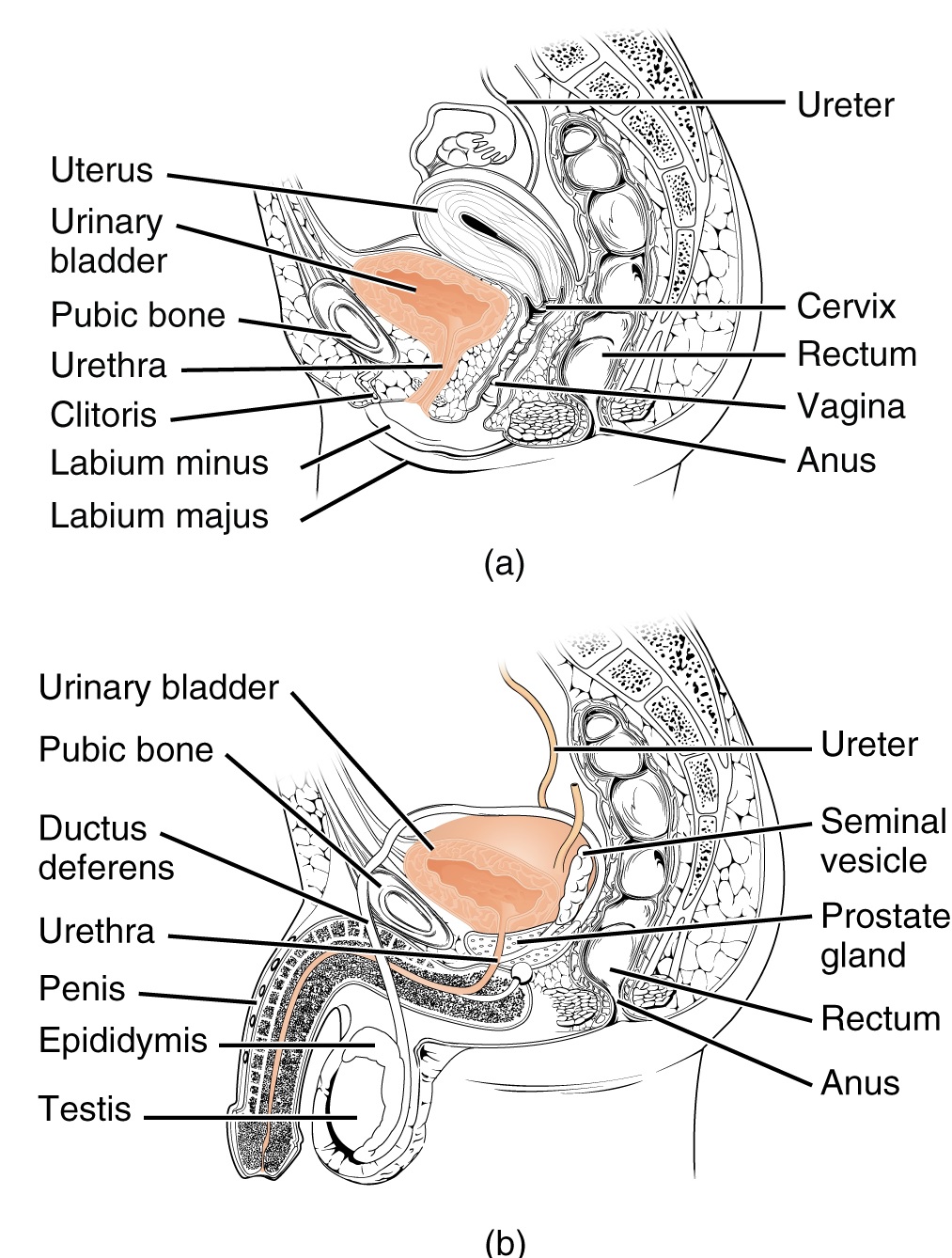
尿道 Urethra
男性:穿前列腺、尿生殖膈、尿道海绵体
◆是排尿、排精的通道,长约16-22 cm
◆有三个狭窄、三个扩大、两个弯曲
女性:尿道穿尿生殖膈
◆短、宽、直,仅有排尿功能 全长3-5 cm,直径0.6 cm 起于尿道内口 ,开口于尿道外口 女性尿道短、宽且直易患逆向尿道感染
Urethra
Male: through the prostate, urogenital diaphragm, corpus spongiosum
◆It is the channel for urination and ejaculation, about 16-22 cm long
◆There are three narrow, three wide, and two bends
Female: urethra through the urogenital diaphragm
◆Short, wide, straight, only urination function Total length 3-5 cm, diameter 0.6 cm Starts at the internal urethra opening and opens at the external urethra opening Female urethra is short, wide and straight and is prone to retrograde urethral infection
Serving Victoria, BC, Saanich, and Oak Bay areas. Address: 1748 Blair Ave, Victoria, BC
Copyright 2026 Jin Tripp Health Services - Privacy policy