TCM Acupuncture Comprehensive Review
TCM Acupuncture Comprehensive Review will summary and review TCM Acupuncture foundation, diagnosis, and Acupuncture Meridians and Points.
We will focus on prepare to pass Pan-Canadian Examinations.
Throughout this course, we will explore the fundamental principles that underpin acupuncture, including the concepts of Qi, meridians, Yin-Yang, and the Five Elements. Understanding these concepts will provide a solid foundation for comprehending the rationale behind acupuncture treatment.
By the end of this comprehensive review, you will have a thorough understanding of TCM acupuncture, its principles, benefits, techniques, and safety considerations.
-
Foundation
-
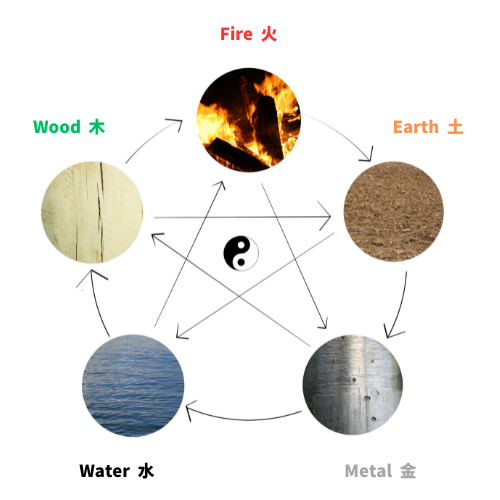
Yin Yang
-
5 Elements
-
Essence Qi-Blood
-
Organgs
Yin Yang
The Yin Yang is a fundamental concept in Chinese philosophy and represents the interdependent nature of opposites.
Yin yang is the basic TCM. The sign of yin and yang are water and fire.
Yang | Yin |
Fire | Water |
Light | Darkness |
Sun | Moon |
Brightness | Shade |
Activity | Rest |
Heaven | Earth |
Round | Flat |
Time | Spacer |
East | West |
South | North |
Left | Right |

Four aspects of Yin–Yang relationship
1. Opposition of Yin and Yang: the opposition is relative, not absolute. |
2. Interdependence of Yin and Yang: one cannot exist without the other. |
3. Mutual consuming of Yin and Yang: Yin is weak, Yang is in apparent excess. |
4. InterTrans formation of Yin and Yang: Yin can change into Yang |
Some of the main correspondences of the Five Elements | |||||
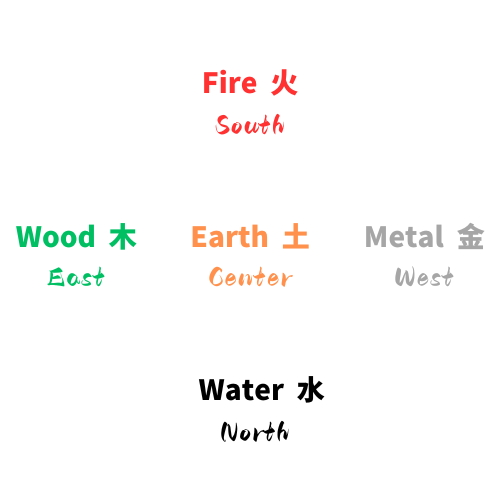
| Wood | Fire | Earth | Metal | Water |
Seasons | Spring | Summer | None | Autumn | Winter |
Colors | Green | Red | Yellow | White | Black |
Directions | East | South | Centre | West | North |
Climates | Wind | Heat | Dampness | Dryness | Cold |
Yin organs | Liver | Heart | Spleen | Lungs | Kidneys |
Yang organs | Gall Bladder | Small Intestine | Stomach | Large Intestine | Bladder |
Sense organs | Eyes | Tongue | Mouth | Nose | Ears |
Tissues | Sinews | Vessels | Muscles | Skin | Bones |
Tastes | Sour | Bitter | Sweet | Pungent | Salty |
Body Fluid | Tear | Sweat | saliva | Nasal discharge | spit |
The Five Elements in physiology
Generating sequence
Controlling sequence
The Five Elements in pathology
The Over-acting sequence
The insulting sequence
Physiology | Pathology |
Generating (Promoting) | The Mother is not nourishing the Son |
The Son is taking too much from the Mother | |
Controlling (Acting) | Over Controlling (Over-acting) |
Insulting (Counter-acting) |
1. Pre-Heaven Essence
2. Post-Heaven Essence
Functions of Essence:
• Growth, reproduction and development
• Basis of Kidney-Qi
• Producer of Marrow
• Basis of constitutional strength
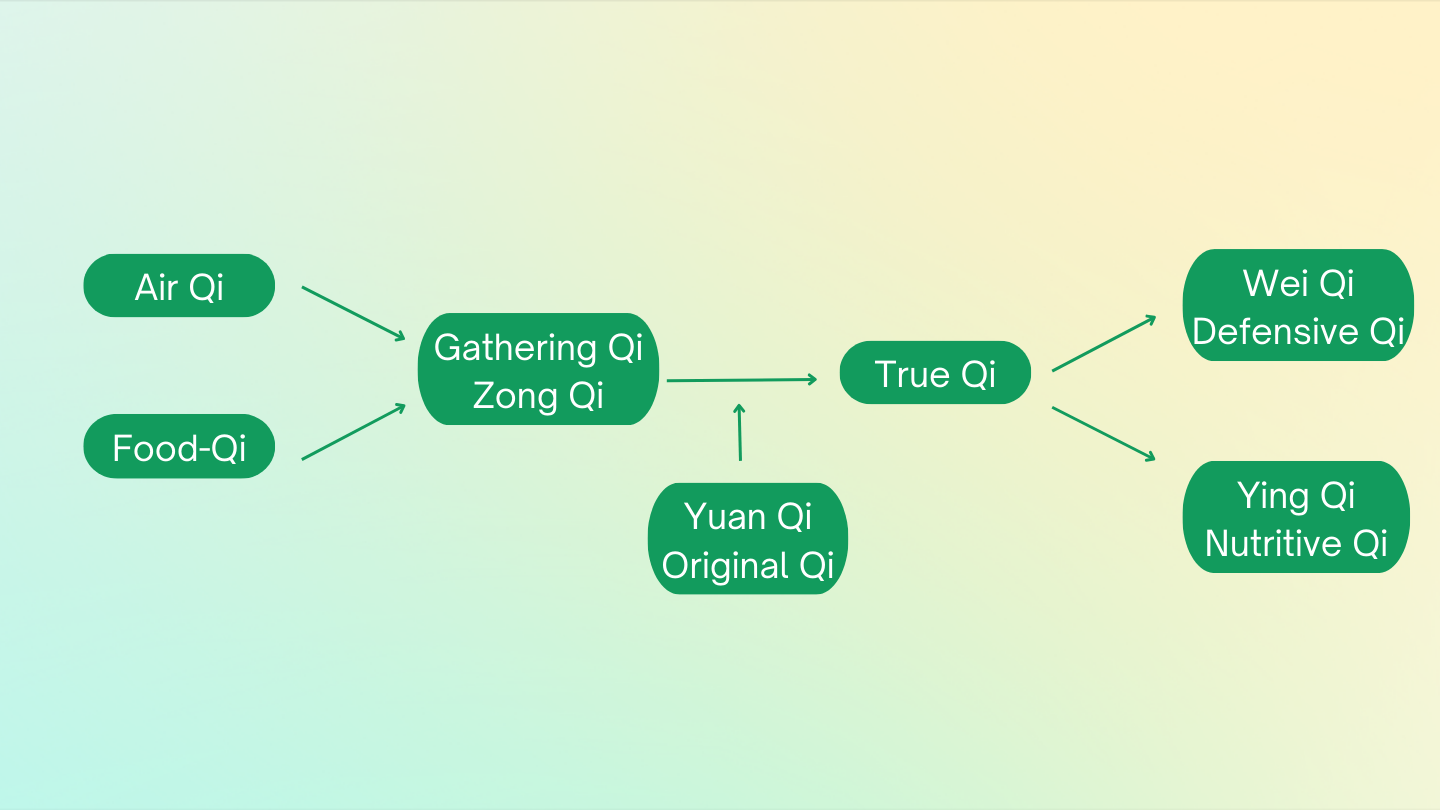
Qi
Nutritive Qi (Ying Qi)
• Nourishes the Internal Organs
• Is closely linked to Blood
• Flows in channels and blood vessels
Defensive Qi (Wei Qi)
• It circulates outside the channels in the space between skin and muscles
• It protects the body from invasion of external pathogenic factors
• It warms the muscles
• It regulates the opening and closing of pores
• It circulates 50 times in 24 hours: 25 during the day and 25 at night
Functions of Qi
• Transforming
• Transporting
• Holding
• Raising
• Protecting
• Warming
Blood
Functions of Blood
• Nourishes the body
• Circulates with Nutritive Qi (Ying Qi)
• Moistens the body
• Houses the Mind
• Determines menstruation
Blood with internal organs
Blood–Qi relationship
Qi generates Blood
Qi moves Blood
Qi holds the Blood
Blood nourishes Qi
Body Fluids
Body Fluids originate from our food and drink.
Types of body fluids
Fluids (Jin): clear, light and watery, they circulate with Defensive Qi in the space between skin and muscles. They moisten skin and muscles
Liquids (Ye): turbid, heavy and dense, they circulate with Nutritive Qi in the Interior. They moisten brain, spine, bone marrow, joints and sense organs.
Relations with internal organs
LU -- diffuse
SP --Transform/transport
KD -- Transform/ separate/excrete
Bladder -- Excretes
Triple Burner --Transforms/ transports/excretes
Stomach -- Origin of Body Fluid
There are 12 organs, six Yin and six Yang:
Yin organs | Yang organs | Element |
Heart Small | Intestine | Emperor Fire |
Liver | Gall Bladder | Wood |
Lungs | Large Intestine | Metal |
Spleen | Stomach | Earth |
Kidneys | Bladder | Water |
Pericardium | Triple Burner | Minister Fire |
The functions of the Heart discussed are:
• The Heart governs Blood
• The Heart controls the blood vessels
• The Heart manifests in the complexion
• The Heart houses the Mind
• The Heart is related to joy
• The Heart opens into the tongue
• The Heart controls sweat
The functions of the Liver
It stores Blood
It ensures the smooth flow of Qi
It controls the sinews
It manifests in the nails
It opens into the eyes
It controls tears
It is affected by anger
Its colour is green
Its taste is sour
Its climate is wind
Functions of the Lungs
They govern Qi and respiration
They control the diffusing and descending of Qi
They regulate the Water passages
They control the skin and the space between skin and muscles
They manifest in the body hair
They open into the nose
They are affected by worry, sadness and grief
Their colour is white
Their taste is pungent
Their climate is dryness
Functions of the Spleen
Governs transformation and transportation
Controls the ascending of Qi
Controls Blood
Controls the muscles and the four limbs
Opens into the mouth
Manifests in the lips
Controls saliva
Controls the raising of Qi
It is affected by pensiveness
Its colour is yellow
Its taste is sweet
Its climate is Dampness
Functions of the Kidney
Store the Essence and govern birth, growth, reproduction and development
Produce Marrow, fill up the brain and control bones
Govern Water
Control the reception of Qi
Open into the ears
Manifest in the hair
Control spittle
Control the two lower orifices
Control the Gate of Life (Minister Fire, Ming Men)
Its colour is black
Its taste is salty
Its climate is cold
The Functions of the Stomach
1. Controls ‘receiving’
2. Controls the ‘rotting and ripening’of food
3. Controls the transportation of food essences
4. Controls the descending of Qi
5. Is the origin of fluids
The Functions of the Small Intestine
1. Controls receiving and transforming
2. Separates fluids
The Functions of the Large Intestine
Transforms stools and reabsorbs fluids
The Functions of the Gall Bladder
1. Stores and excretes bile
2. Controls decisiveness
The Functions of the Bladder
Removes Water by Qi transformation
The Six Extraordinary Yang Organs
• Uterus
• Brain
• Marrow
• Bones
• Blood Vessels
• Gall Bladder
• Uterus
The Uterus is related to the Kidneys, in males it is called Dan Tian or also Room of Essence, in females it is called Uterus.
The functions of the Uterus:
In female:
It regulates menstruation
It houses the fetus during pregnancy
In male:
The ‘Room of Essence’ in men stores and produces sperm and is closely related to the Kidneys and the
Governing Vessel. If the Kidneys and the Governing Vessel (Du Mai) are empty, the production and storage of sperm by the Room of Essence will be affected, and this may cause impotence, premature ejaculation, clear and watery sperm, nocturnal emissions, spermatorrhoea, etc.
• Brain
The functions of the Brain are:
• It controls intelligence
• It is the Sea of Marrow and controls sight, hearing, smell and taste
• Marrow
The functions of Marrow:
• It contributes to making Blood
• It nourishes the Brain
• Bones
The Bones are like a trunk, structural framework of the body.
The Bones are the cavity that houses Marrow and, as such, they are also functionally related to the Kidneys.
• Blood Vessels
The functions of the Blood Vessels:
• They house Blood and are the vehicle for the circulation of Qi and Blood
• They transport refined food essences, Qi and Blood all over the body
• Gall Bladder
-
Diagnosis
-
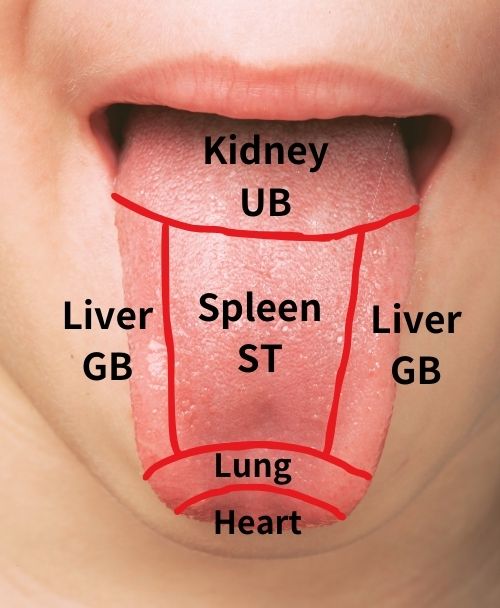
Inspection (Tongue)
-
Hearing and smelling
-
inquiring
-
Palpation (Pulse)
Observation:
Spirit | Body | movement | Head | face |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Eyes | Nose | Ears | Mouth | Teeth |
Throat | Limbs | Skin | Tongue | Channels |
The observation of ‘spirit’ (shen):
• Complexion with spirit has lustre; without spirit, no lustre, dull
• Eyes with spirit have lustre and brightness; without spirit, dull, clouded
• State of mind with spirit is alert and clear; without spirit, dull and depressed
• Breathing with spirit is even; without spirit is laboured
The normal complexion:
• Lustre
• A subtle, slightly reddish hue
• Moisture
Pathological colors:
• White • Yellow • Red • Green • Blue • Black
White complexion
• Blood deficiency (dull-white)
• Yang deficiency (bright-white)
• Yang deficiency with Cold (bluish-white)
Yellow complexion
• Spleen deficiency (sallow yellow)
• Damp-Heat with prevalence of Heat (bright orange-yellow)
• Damp-Heat with prevalence of Dampness (smoky, dull-yellow)
• Heat in Stomach and Spleen (withered, dried-up yellow)
• Cold-Dampness in Stomach and Spleen (dull-pale yellow)
• Spleen deficiency (pale yellow )
Red complexion
• Full-Heat: whole face red
• Empty-Heat: red cheek bones
Green complexion
• Liver patterns
• Interior Cold
• Pain
• Interior Wind
Blue complexion
• Cold in Liver channel (dark-bluish under the eyes)
• Cold or chronic pain (white-bluish)
• Severe Heart-Yang deficiency with Blood stasis (dull-bluish)
• Liver Wind (bluish complexion, in children)
Black complexion
• Cold: black and moist
• Heat: black and dried-up, burned-looking
• Kidney deficiency: Dark with low back pain
• Blood Stasis: Dark without brightness + scaly skin
Eyes
Eyes are clear and have luster indicate have Shen.
Eyes are rather dull or clouded, it shows disturbed Shen.
A red colour in the corners of the eye indicates Heart- Fire;
a red colour in the sclera indicates Lung-Heat.
A yellow colour of the sclera indicates Damp-Heat.
If the whole eye is red, painful and swollen, it indicates either an exterior invasion of Wind-Heat or rising of Liver-Fire.
A dull-white color of the corners indicates Heat and a pale-white color indicates Blood deficiency.
Infant Finger Venules
Venule observation is a diagnostic method that can replace pulse diagnosis for children under 3 years old.
vein near LI meridian on radial side.
if it is not present = not diseased or in poor health
- first wind gate/feng guan: exterior /mild pathology
- second gate/qi guan: more interior and more severe
- third gate is life/ming gate: severe internal condition,life threatening
- Slightly red =Cold, Dark red/purple = Heat
- shallow – EPI
- deep – internal
Tongue
Tongue-body color
Pale tongue
• Yang deficiency (slightly wet)
• Blood deficiency (slightly dry)
• Pale sides: Liver-Blood deficiency
Purple tongue
• Always indicates Blood stasis
• Reddish-Purple: Blood stasis from Heat
• Bluish-Purple: Blood stasis from Cold
• Reddish-Purple sides: Liver-Blood stasis
• Bluish-Purple sides in a woman: Blood stasis in the Uterus
Red tongue
• Red: Heat
• Red with coating: Full-Heat
• Red without coating: Empty-Heat
• Red tip: Heart-Fire or Heart Empty-Heat (coating: latter without)
• Red sides with coating: Liver-Fire or Gall-Bladder Heat
• Red sides without coating: Liver-Yin deficiency with Empty-Heat
• Red Centre: Heat or Empty-Heat of the Stomach (depending on whether there is a coating or not)
• Red points on the tip: Heart-Fire
• Red points on the sides: Liver-Fire
• Red spots on the root: Heat in the Lower Burner
• Red points in or around the center: Stomach-Heat
Tongue-body shape
• Thin: Blood or Yin deficiency (Pale or Red without coating, respectively)
• Swollen: Dampness or Phlegm
• Partially swollen: Heat
• Stiff: interior Wind or Blood stasis
• Flaccid: deficiency of Body Fluids
• Short: severe Yang or Yin deficiency (Pale or Red without coating, respectively)
• Cracked: Heat or Yin deficiency
• Deviated: interior Wind
• Tooth-marked: Spleen-Qi deficiency
Tongue coating:
• Normal coating is thin white
• Thick coating: pathogenic factor (the thicker the coating, the stronger the pathogenic factor)
• Absence of coating: Stomach-Yin deficiency
• Total absence of coating, Red tongue body: Stomach- and Kidney-Yin deficiency with Empty-Heat
• White coating: Cold pattern
• Yellow coating: Full-Heat pattern
• Grey and black coating: extreme Cold or extreme Heat (tongue wet or dry, respectively)
Moisture of tongue
• Indicates state of Body Fluids
• Normal tongue is slightly moist
• Too wet: Yang deficiency
• Too dry: Heat or Yin deficiency
• Sticky/slippery: Dampness and/or Phlegm
Diagnosis by hearing
Voice
Breathing
Cough
Vomiting
Hiccup
Borborygmi
Sighing
Belching
Voice
• Loud voice: Full pattern
• Weak voice: Empty pattern
• Reluctance to talk: Cold pattern or Lung-Qi deficiency
• Excessive talking: Heat
• Sudden loss of voice: invasion of Wind-Heat
• Gradual loss of voice: Lung-Qi or Lung-Yin deficiency
Diagnosis by smelling
Body odour
Odour of bodily secretions
• Breath
• Sweat
• Sputum
• Urine and stools
• Vaginal discharge
• Intestinal gas
Breath smells
• Strong, foul: Stomach-Heat or retention of food
• Sour: retention of food, Accumulation Disorder (in children)
• Foul, pungent: Damp-Heat in Stomach and Spleen
The 16 questions
1. Pain
2. Food and taste
3. Stools and urine
4. Thirst and drink
5. Energy levels
6. Head, face and body
7. Chest and abdomen
8. Limbs
9. Sleep
10. Sweating
11. Ears and eyes
12. Feeling of cold, feeling of heat and fever
13. Emotional symptoms
14. Sexual symptoms
15. Women’s symptoms
16. Children’s symptoms
Causes of pain
• Qi stagnation: distension more than pain, or a distending pain, no fixed location, coming and going
• Liver-Yang rising: chronic headaches with a distending, throbbing pain
• Blood stasis: severe, stabbing pain, with a fixed location
• Cold (Full or Empty): cramping, spastic pain aggravated by cold weather and cold foods/liquids and alleviated by the application of heat
• Damp-Heat: burning pain with a feeling of fullness and heaviness
• External Wind: occipital headache and stiffness
• External Dampness: pain in the joints or epigastrium
• Retention of food: intense pain with feeling of fullness (more in children)
• Phlegm: does not usually cause pain, but it may do so especially in the joints (as in rheumatoid arthritis)
Taste
• Lack of taste sensation: Spleen and Stomach deficiency
• Bitter taste: Heat in Liver or Heart
• Sweet taste: Spleen deficiency or Damp-Heat
• Sour taste: retention of food or Liver invading Stomach
• Salty taste: Kidney-Yin deficiency
• Pungent taste: Lung-Heat
Food
• Condition relieved by eating: Empty
• Condition aggravated by eating: Full
• Lack of appetite: Spleen-Qi deficiency
• Excessive hunger: Stomach-Heat
• Feeling of fullness: Dampness or retention of food
• Feeling of distension: Qi stagnation
• Preference for hot foods/drinks: Cold pattern
• Preference for cold foods/liquids: Heat pattern
Vomiting
• Sour vomiting: invasion of Stomach by Liver
• Bitter vomiting: Liver and Gall Bladder-Heat
• Clear watery vomiting: Cold in the Stomach with retention of fluids
• Vomiting soon after eating: Heat pattern
Constipation
• Aggravation of a condition after a bowel movement: Empty pattern
• Amelioration of a condition after a bowel movement: Full condition
• Acute constipation with thirst and dry yellow coating: Heat in the Stomach and Intestines
• Constipation in old people or women after childbirth: deficiency of Blood
• Constipation with small, dry, bitty stools like goat’s stools indicates stagnation of Liver-Qi and Heat in the Intestines
• Difficulty in performing a bowel movement (stools not dry): stagnation of Liver-Qi
• Constipation with abdominal pain: internal Cold, which may be Full or Empty
• Constipation with dry stools, dry mouth, desire to drink in small sips: Yin deficiency, usually of Kidneys and/or Stomach
• Alternation of constipation and diarrhea: stagnant Liver-Qi invading the Spleen
Loose stools/diarrhea
• Chronic loose stools/diarrhea: Spleen- and/or Kidney-Yang deficiency
• Chronic diarrhea every day in the very early morning: Kidney-Yang deficiency
• Diarrhea with abdominal pain: interior Cold in the Intestines
• Diarrhea with mucus in the stools: Dampness in the Intestines
• Diarrhea with mucus and blood in the stools: Damp-Heat in the Intestines
• Loose stools with undigested food: Spleen-Qi deficiency
• Stools not loose or only slightly loose but very frequent, deficiency of Spleen with sinking of Spleen-Qi
• Foul-smelling stools: Heat
• Absence of smell: Cold
• Borborygmi with loose stools: Spleen deficiency
• Borborygmi with abdominal distension and without loose stools: stagnation of Liver-Qi
• Burning sensation in the anus while passing stools: Heat
Thirst and drink
• Thirst with desire to drink large amounts of cold water: Full-Heat pattern
• Thirst with desire to drink in small sips: Yin deficiency (usually of Stomach or Kidneys)
• Absence of thirst: Cold pattern, usually of the Stomach or Spleen
• Thirst but with no desire to drink: Damp-Heat
• Desire to drink cold liquids: Heat pattern
• Desire to drink warm liquids: Cold pattern
Headache
Onset
• Recent onset, short duration: headache from exterior attack of Wind-Cold
• Gradual onset, in attacks: interior type
Time of day
• Daytime: Qi or Yang deficiency
• Evening: Blood or Yin deficiency
• Night-time: Blood stasis
Location
• Nape of neck: Greater Yang channels (can be from exterior invasion of Wind-Cold, or from interior Kidney deficiency)
• Forehead: Bright Yang channels (can be from Stomach-Heat or Blood deficiency)
• Temples and sides of head: Lesser Yang channels (can be from exterior Wind in the Lesser Yang, or from interior Liver and Gall Bladder Fire rising)
• Vertex: Terminal Yin channels (usually from deficiency of Liver-Blood)
• Whole head: exterior invasion of Wind-Cold
Character of pain
• Heavy feeling: Dampness or Phlegm
• Pain which is ‘inside’ the head, ‘hurting the brain’: Kidney deficiency
• Distending, throbbing: rising of Liver-Yang
• Boring, like a nail in a small point: stasis of Blood
• With a feeling of muzziness and heaviness: Dampness
• With a feeling of muzziness, heaviness and dizziness: Phlegm
Condition
• With aversion to wind or cold: exterior invasion
• Aggravated by cold: Cold pattern
• Aggravated by heat: Heat pattern
• Aggravated by fatigue, improved by rest: Qi deficiency
• Aggravated by emotional tension: Liver-Yang rising
• Aggravated by sexual activity: Kidney deficiency
Dizziness
• Severe giddiness when everything seems to sway and the person loses the balance: internal Wind
• Dizziness with throbbing headaches: Liver-Yang rising
• Dizziness accompanied by a feeling of heaviness and muzziness : Phlegm obstructing the head
• Slight dizziness aggravated when tired: indicates Qi and Blood deficiency
• Sudden onset: Full pattern
• Gradual onset: Empty pattern
Sweating
Full
• Heat
• Damp-Heat
Empty
• Deficiency of Yang
• Deficiency of Yin
Tinnitus
Onset
• Sudden onset: Full condition, Liver-Fire, Liver-Yang rising, Liver-Wind
• Gradual onset: Empty condition, Kidney deficiency
Pressure
• Noise aggravated by pressing with one’s hands on the ears: Full condition
• Noise alleviated by pressing with one’s hands on the ears: Empty condition
Character
• Loud, high-pitched noise, like whistle: Liver-Yang, Liver-Fire, Liver-Wind
• Low-pitched noise like rushing water: Kidney deficiency
Deafness
• Sudden onset: Full condition, Liver-Fire, Liver-Yang rising, Liver-Wind
• Gradual onset: Empty condition, deficiency of Kidneys, Blood or Qi deficiency
Menstruation
Cycle
• Periods always early: Blood-Heat or Qi deficiency
• Periods always late: Blood deficiency or stagnation of Blood or Cold
• Periods irregular, sometimes early and sometimes late: stagnation of Liver-Qi or Liver-Blood, or Spleen deficiency
Amount
• Heavy loss of blood: Blood-Heat or Qi deficiency
• Scanty periods: Blood deficiency or stagnation of Blood or Cold
Colour
• Dark-red or bright-red: Blood-Heat
• Pale: Blood deficiency
• Purple or blackish blood: stasis of Blood or Cold
• Fresh-red: Empty-Heat from Yin deficiency
Quality
• Congealed blood with clots: stasis of Blood or Cold
• Watery blood: Blood or Yin deficiency
Pain
• Before the periods: stagnation of Qi or Blood
• During the periods: Blood-Heat or stagnation of Cold
• After the periods: Blood deficiency
• Pulse
• Skin
• Limbs
• Chest
• Abdomen
• Points
Pulse
Right | Left | |
|---|---|---|
LU | Cun | HT |
SP | Guan | LV |
MM | Chi | KD |
The normal pulse
The pulse should have three qualities, which are described as having Stomach-Qi, having spirit and
having a root.
1. Floating (Fu)
Feeling
This pulse can be felt with a light pressure of the fingers, just resting the fingers on the artery.
• Invasion of external Wind
• Yin deficiency (interior conditions)
2. Deep (Chen)
Feeling
it can only be felt with a heavy pressure of the fingers and is felt near the bone.
• Pathogenic factor in the Interior (Deep-Full)
• Yang deficiency (Deep-Weak)
3. Slow (Chi)
Feeling
This pulse has three beats per respiration cycle (of the practitioner).
• Cold pattern
• Empty-Cold (Slow and Weak)
• Full-Cold (Slow and Full)
4. Rapid (Shu)
Feeling
This pulse has higher rate than normal, five beats per each respiration cycle or more.
Rapid pulse
• Heat pattern
• Full-Heat (Rapid and Full)
• Empty-Heat (Rapid and Floating-Empty)
5. Empty (Xu)
Feeling
The Empty pulse feels rather big but soft. this pulse is actually rather big but it feels empty on a slightly stronger pressure and is soft.
Empty pulse
• Qi deficiency
6. Full (Shi)
Feeling
This pulse feels full, rather hard and rather long.
‘Full’ is often used in two slightly different ways.
On the one hand, this term is often used to indicate any pulse of the Full type.
• Full pattern
• Full-Heat (Full-Rapid)
• Full-Cold (Full-Slow)
7. Slippery (Hua)
Feeling
A Slippery pulse feels smooth, rounded, slippery to the touch, as if it were oily. It slides under the fingers.
• Phlegm
• Dampness
• Retention of food
• Pregnancy
8. Choppy (Se)
Feeling
This pulse feels rough under the finger: instead of a smooth pulse wave, it feels as if it has a jagged edge to it.
Choppy also indicates a pulse that changes rapidly both in rate and quality.
• Blood deficiency
• Exhaustion of Body Fluids
9. Long (Chang)
Feeling
This pulse is basically longer than normal: it extends slightly beyond the normal pulse position.
• Heat pattern
10. Short (Duan)
Feeling
It occupies a shorter space than the normal position.
• Severe Qi deficiency
• Stomach-Qi deficiency
11. Overflowing (Hong)
Feeling
This pulse feels big. It extends beyond the pulse position. It is superficial and generally feels as if it overflows the normal pulse channel, like a river overflow during a flood.
• Full-Heat
• Empty-Heat (Overflowing-Empty)
12. Fine (Xi)
Feeling
This pulse is thinner than normal.
• Blood deficiency
• Dampness with severe Qi deficiency
13. Minute (Wei)
Feeling
It is extremely thin, small and difficult to feel.
• Severe deficiency of Qi and Blood
14. Tight (Jin)
Feeling
This pulse feels twisted like a thick rope.
• Cold
• Exterior Cold (Tight-Floating)
• Interior Full-Cold (Tight-Full-Deep)
• Interior Empty-Cold (Tight-Weak-Deep)
• Pain
15. Wiry (Xian)
Feeling
This pulse feels taut like a guitar string. It is thinner, more taut and harder than the Tight pulse. The Wiry pulse really hits the fingers.
• Liver disharmony
• Pain
• Phlegm
16. Slowed down (Huan)
Feeling
This pulse has four beats for each respiration cycle.
• Generally, a healthy pulse
17. Hollow (Kou)
Feeling
This pulse can be felt at the superficial level, but if one presses slightly harder to find the middle level it is not there; it is then felt again at the deep level with a stronger pressure. In other words, it is Empty in the middle.
• Haemorrhage
• Forthcoming haemorrhage (Hollow and Rapid)
18. Leather (Ge)
Feeling
This pulse feels hard and tight at the superficial level and stretched like a drum, but it feels completely Empty at the deep level. It is a large pulse, not thin.
• Severe deficiency of Kidney-Essence
• Severe deficiency of Kidney-Yin
19. Firm (Lao)
Feeling
The Firm pulse is felt only at the deep level and it feels hard and rather wiry. It could be described as a Wiry pulse at the deep level.
• Blood stasis
• Interior Cold (Firm and Slow)
• Pain
20. Soggy (or Weak-Floating) (Ru)
Feeling
The Soggy pulse can be felt only on the superficial level. It feels very soft and is only slightly floating: It disappears when a
stronger pressure is applied to feel the deep level. It is similar to the Floating-Empty pulse, but it is softer and not so Floating.
• Dampness with Qi deficiency
• Deficiency of Yin
• Deficiency of Essence
21. Weak (Ruo)
Feeling
A Weak pulse cannot be felt on the superficial level, but only at the deep level. It is also soft.
• Yang deficiency
• Blood deficiency
22. Scattered (San)
Feeling
This pulse feels very small and is relatively superficial.nstead of feeling like a wave, the pulse feels as if it were ‘broken’ in small dots.
• Severe deficiency of Qi and Blood
• Severe deficiency of Kidney-Qi
• Serious condition
23. Hidden (Fu)
Feeling
This pulse feels as if it were hidden beneath the bone.
It is very deep and difficult to feel. It is basically an extreme case of a Deep pulse.
• Severe Yang deficiency
24. Moving (Dong)
Feeling
The Moving pulse has a round shape like a bean; it is short and it ‘trembles’ under the finger. It has no definite shape, having no head or tail, just rising up in the centre. It feels as if it is shaking and is also somewhat slippery.
• Shock, anxiety, fright
• Pain
25. Hasty (Cu)
Feeling
This pulse is Rapid and it stops at irregular intervals.
• Severe Heat
• Deficiency of Heart-Qi
• Heart-Fire
26. Knotted (Jie)
Feeling
This pulse is Slow and it stops at irregular intervals.
• Cold with deficiency of Heart-Yang
27. Intermittent (Dai)
Feeling
This pulse stops at regular intervals.
• Serious problem in Internal Organ
• Heart problem (in Western medical sense)
28. Hurried (Ji)
Feeling
This pulse is very rapid, but it also feels very agitated and urgent.
• Fire exhausting Yin
-
Patterns
-
Eight Principles
-
Qi Blood Body Fluid
-
Zhang - Fu
-
SIX - Channels
-
Four Levels
The Eight Principles
1. Interior–Exterior
2. Hot–Cold
3. Full–Empty (or Excess–Deficiency)
4. Yin–Yang
1. Interior–Exterior
Skin, muscles and channels are the ‘Exterior’ of the body, and the Internal Organs the ‘Interior’.
Clinical manifestations of exterior patterns
Aversion to cold, ‘fever’, aching body, a stiff neck and a Floating pulse
Clinical manifestations of exterior Cold pattern
Slight ‘fever’, pronounced aversion to cold, severe aches in the body, severe stiff neck, no sweating, no thirst, a Floating-Tight pulse and a thin white tongue coating
Clinical manifestations of exterior Heat pattern
Aversion to cold, ‘fever’, slight sweating, thirst, a Floating-Rapid pulse, a thin white tongue coating and sometimes redness of the tongue on the sides and/or front
2. Hot–Cold
Full-Heat
Manifestations
• Thirst, a feeling of heat, mental restlessness, red face, dry stools, scanty dark urine, Rapid-Full pulse, Red tongue with yellow coating (Internal Full-Heat)
Etiology
• Emotional problems
• Diet (too much red meat, spices, alcohol)
• An external pathogenic factor that has penetrated into the Interior and transformed into Heat
Empty-Heat
Manifestations
• A feeling of heat in the afternoon or evening, a dry mouth with desire to drink in small sips, a dry throat at night, night sweating, a feeling of heat in the chest, palms and soles (five-palm heat), dry stools, scanty dark urine, Floating- Empty and Rapid pulse, Red tongue without coating
Etiology
• Overwork (in the sense of working long hours)
• Irregular eating
• Excessive sexual activity
• Persistent, heavy blood loss (such as in menorrhagia)
Full-Cold
Manifestations
• Feeling cold, cold limbs, no thirst, pale face, abdominal pain aggravated on pressure, desire to drink warm liquids, loose stools, clear abundant urination, Deep-Full-Tight pulse and a Pale tongue with thick white coating (Internal Full-Cold)
Etiology
• Cold foods (salads, fruit, iced drinks)
Empty-Cold
Manifestations
• Feeling cold, cold limbs, a dull pale face, no thirst, listlessness, sweating, loose stools, clear abundant urination, a Deep-Slow or Weak pulse and a Pale tongue with thin white coating
Etiology
• Excessive physical work
• Excessive sexual activity (Kidney-Yang)
• Internal Cold injuring Yang
COMBINED HOT AND COLD
• Cold on the Exterior and Heat in the Interior
• Heat on the Exterior and Cold in the Interior
• Heat above and Cold below
• Combination of Heat and Cold patterns
• False Heat–True Cold and False Cold–True Heat
3. Full–Empty (or Excess–Deficiency)
Full conditions
Acute onset, restlessness, irritability, a strong voice, coarse breathing, pain aggravated by pressure, high-pitched tinnitus, scanty urination, constipation, Full pulse
Empty conditions
1. Empty Qi: • Pale face, weak voice, slight sweating, slight shortness of breath, tiredness, loose stools, poor appetite, Empty pulse
2. Empty Yang: Chilliness, a bright pale face, cold limbs, no thirst, a desire for hot drinks, loose stools, frequent pale urination, a Weak pulse and a Pale and wet tongue (in addition to the manifestations of Empty Qi)
3. Empty Blood: • Dull pale face, pale lips, blurred vision, dry hair, tiredness, poor memory, numbness or tingling, insomnia, scanty periods, Fine or Choppy pulse, Pale-Thin tongue
4. Empty Yin: • Feeling of heat in the afternoon or evening, a dry throat at night, night sweating, thin body, a Floating-Empty pulse and a Red-Peeled and dry tongue
Mixed Full–Empty conditions
Examples
• Kidney-Yin deficiency with Liver-Yang rising
• Liver-Blood deficiency with Liver-Yang rising
• Spleen-Qi deficiency with Phlegm
• Deficiency of Blood with Blood stasis
• Kidney-Yang deficiency with Dampness
4. Yin–Yang
Empty Yin
• Feeling of heat in the afternoon or evening, a dry throat at night, night sweating, thin body, a Floating-Empty pulse and a Red-Peeled and dry tongue
Collapse of Yin
The main manifestations are abundant perspiration, skin hot to the touch, hot limbs, a dry mouth with
desire to drink cold liquids in small sips, retention of urine, constipation, a Floating-Empty and Rapid pulse and a Red-Peeled, Short and Dry tongue.
Empty Yang
• Chilliness, a bright pale face, cold limbs, no thirst, a desire for hot drinks, loose stools, frequent pale urination, a Weak pulse and a Pale and wet tongue (in addition to the manifestations of Empty Qi)
Collapse of Yang
The main manifestations are chilliness, cold limbs, weak breathing, profuse sweating with an oily sweat,
no thirst, frequent profuse urination or incontinence, loose stools or incontinence, a Minute-Deep pulse and a Pale-Wet-Swollen-Short tongue.
Qi pattern identification
Qi deficiency
• Slight shortness of breath, weak voice, spontaneous sweating, poor appetite, loose stools, tiredness, Empty pulse
Qi sinking
• Slight shortness of breath, weak voice, spontaneous sweating, poor appetite, loose stools, tiredness, a feeling of bearing down, mental depression, listlessness, prolapse of an organ, Empty pulse
Qi stagnation
• Feeling of distension, distending pain that moves from place to place, mental depression, irritability, gloomy
feeling, frequent mood swings, frequent sighing, Wiry pulse, tongue body either normal-colored or slightly Red on the sides
Rebellious Qi
Rebellious Qi occurs when Qi flows in the wrong direction (i.e. a direction different from its normal physiological one).
the normal direction of flow of each organ is as follows:
• Spleen-Qi: upwards
• Stomach-Qi: downwards
• Lung-Qi: downwards
• Heart-Qi: downwards
• Liver-Qi: in all directions and upwards
• Intestines Qi: downwards
• Kidney-Qi: downwards (but from some aspects also upwards)
• Bladder-Qi: downwards
BLOOD PATTERN IDENTIFICATION
Blood deficiency
• Dull-white sallow complexion, dizziness, poor memory, numbness or tingling, blurred vision, insomnia, pale lips, scanty periods or amenorrhoea, depression, slight anxiety, Pale and slightly dry tongue, Choppy or Fine pulse
Stasis of Blood
Dark complexion, purple lips, pain which is boring, fixed and stabbing in character, abdominal masses that do not move, purple nails, bleeding with dark blood and dark clots, painful periods with dark clots, Purple tongue, Wiry, Firm or Choppy pulse.
Blood Heat
Feeling of heat, skin diseases with red eruptions, thirst, bleeding, Red tongue, Rapid pulse
Loss of Blood
• Epistaxis (nose), haematemesis (ST), haemoptysis (Lung), melaena (Stool), menorrhagia, haematuria
Body Fluid pattern identification
Deficiency of Body Fluids may be caused by dietary factors (excessive consumption of drying foods It may also arise from a heavy and prolonged loss of fluids such as in sweating, vomiting and diarrhea.
It is also derived from a heavy, acute loss of Blood, such as during childbirth, or from a heavy, chronic loss of Blood such as in menorrhagia.
Severe and chronic deficiency of Blood can cause dryness and deficiency of fluids
Deficiency of Body Fluids
Dry skin, mouth, nose, cough, lips, dry tongue
Oedema
Oedema arises from a Yang deficiency of either Spleen, Lungs or Kidneys or all three of them.
• Lung-Yang deficiency: oedema of face and hands
• Spleen-Yang deficiency: abdomen and limbs
• Kidney-Yang deficiency: lower part of the body, the legs and ankles
• Pitting: deficiency of Yang of Spleen, Lungs and/or Kidneys
• Non-pitting: Qi stagnation or Dampness
Essential manifestations of Phlegm
• Tongue and pulse: Swollen tongue body with sticky tongue coating; Slippery or Wiry pulse
• Other symptoms: a feeling of oppression of the chest, nausea, a feeling of heaviness, a feeling of muzziness of the head and dizziness
Substantial Phlegm
Substantial Phlegm is Phlegm in the Lungs.
Non-substantial Phlegm
Under the skin: Lumps under the skin, nerve ganglia swellings, swelling of lymph nodes, swelling of the thyroid, lipoma
In the channels: Numbness
Misting the Heart: Mental illness
In Gall Bladder or Kidneys: Gall bladder or kidney stones
In the joints: Bone deformities in chronic rheumatoid arthritis
LV Full patterns
Liver-Qi stagnation
Clinical manifestations
1. Feeling of distension of hypochondrium, chest, epigastrium or abdomen
2. Depression, moodiness, fluctuation of mental state, feeling of lump in the throat
3. Irregular periods, distension of breasts before the periods, premenstrual tension and irritability
Tongue: the body colour may be normal. In severe cases, it may be slightly Red on the sides
Pulse: Wiry, especially on the left side
Stagnant Liver-Qi turning into Heat
Clinical manifestations
Hypochondrial or epigastric distension, a slight feeling of oppression of the chest, irritability, melancholy, depression, moodiness, a feeling of lump in the throat, a feeling of heat, red face, thirst, propensity to outbursts of anger, premenstrual tension, irregular periods, premenstrual breast distension, heavy periods, tongue Red on the sides, Wiry pulse
Liver-Blood stasis
Clinical manifestations
Hypochondrial pain, abdominal pain, vomiting of blood, epistaxis, painful periods, irregular periods, dark and clotted menstrual blood, infertility, masses in abdomen, purple nails, purple lips, purple or dark complexion, dry skin (in severe cases), Purple tongue, Wiry or Firm pulse
Liver-Fire blazing
Clinical manifestations
Irritability, propensity to outbursts of anger, tinnitus, deafness, temporal headache, dizziness, red face and eyes, thirst, bitter taste, dream-disturbed sleep, constipation with dry stools, dark-yellow urine, epistaxis(nose), haematemesis(vomit), haemoptysis(cough), Red tongue, redder on the sides, dry yellow coating, Full-Wiry- Rapid pulse
Damp-Heat in the Liver
Clinical manifestations
Fullness of the hypochondrium, abdomen or hypogastrium, bitter taste, sticky taste, poor appetite, nausea, feeling of heaviness of the body, yellow vaginal discharge, vaginal itching, vulvar eczema or sores, mid-cycle bleeding and/or pain, pain, redness and swelling of the scrotum, genital, papular or vesicular skin rashes and itching, urinary difficulty, burning on urination, dark urine, Red tongue with redder sides, sticky yellow coating, Slippery-Wiry-Rapid pulse
Stagnation of Cold in the Liver channel
Clinical manifestations
Fullness and distension of the hypogastrium with pain which refers downwards to the scrotum and testis and upwards to the hypochondrium, the pain is alleviated by warmth, straining of the testis or contraction of the scrotum, vertical headache, feeling of cold, cold hands and feet, vomiting of clear watery fluid or dry vomiting. In women there can be shrinking of the vagina, Pale and wet tongue with a white coating, Deep-Wiry-Slow pulse
LV Empty patterns
Liver-Blood deficiency
Clinical manifestations
Dizziness, numbness or tingling of limbs, insomnia, blurred vision, ‘floaters’ in eyes, diminished night vision, scanty menstruation or amenorrhoea, dull-pale complexion without lustre, pale lips, muscular weakness, cramps, withered and brittle nails, dry hair and skin, depression, a feeling of aimlessness, Pale tongue, Thin and slightly dry, Choppy or Fine pulse
Liver-Yin deficiency
Clinical manifestations
Dizziness, numbness or tingling of limbs, insomnia, blurred vision, ‘floaters’ in eyes, dry eyes, diminished night vision, scanty menstruation or amenorrhoea, dull-pale complexion without luster but with red cheekbones, muscular weakness, cramps, withered and brittle nails, very dry hair and skin, depression, a feeling of aimlessness, red tongue without coating or with rootless coating, Floating-Empty pulse
Full/Empty patterns
Liver-Yang rising
a) Liver-Yang rising deriving from Liver-Yin deficiency
b) Liver-Yang rising deriving from Liver- and Kidney-Yin deficiency
c) Liver-Yang rising deriving from Liver-Blood deficiency
Liver-Wind
• Extreme Heat generating Wind
• Liver-Yang rising generating Wind
• Liver-Fire generating Wind
• Liver-Blood deficiency generating Wind
Gall Bladder Full patterns
Dampness in the Gall Bladder
Clinical manifestations
Jaundice, dull-yellow eyes and skin, hypochondrial pain, fullness and distension, nausea, vomiting, inability to digest fats, dull-yellow sclera, turbid urine, no thirst, sticky taste, dull headache, feeling of heaviness of the body, thick sticky white tongue coating, either bilateral in two strips or unilateral, Slippery-Wiry pulse
Damp-Heat in the Gall Bladder
Clinical manifestations
Hypochondrial pain, fullness and distension, nausea, vomiting, inability to digest fats, yellow complexion, scanty and dark yellow urine, fever, thirst without desire to drink, bitter taste, dizziness, tinnitus, irritability, feeling of heaviness of the body, numbness of the limbs, swelling of the feet, loose stools or constipation, alternation of hot and cold feeling, yellow sclera, feeling of heat, thick sticky yellow tongue coating, either bilateral in two strips or unilateral, Slippery-Wiry-Rapid pulse
Empty patterns
Gall Bladder deficient
Clinical manifestations
Dizziness, blurred vision, floaters, nervousness, timidity, propensity to being easily startled, lack of courage and initiative, indecision, sighing, waking up early in the morning, restless dreams, tongue Pale or normal, Weak pulse
HT Deficiency patterns
Heart-Qi deficiency
Clinical manifestations
Palpitations, shortness of breath on exertion, pale face, spontaneous sweating, tiredness, slight depression, Pale tongue, Empty pulse
Heart-Yang deficiency
Clinical manifestations
Palpitations, shortness of breath on exertion, tiredness, spontaneous sweating, a slight feeling of stuffiness or discomfort in the heart region, feeling of cold, cold hands, bright-pale face, slightly dark lips, Pale tongue, Deep-Weak pulse
Heart-Yang Collapse
Clinical manifestations
Palpitations, shortness of breath, weak and shallow breathing, profuse sweating, cold limbs, cyanosis of lips, greyish-white complexion, in severe cases coma, very Pale or Bluish tongue, Hidden-Minute-Knotted pulse
Heart-Blood deficiency
Clinical manifestations
Palpitations, dizziness, insomnia, dream-disturbed sleep, poor memory, anxiety, propensity to be startled, dull-pale complexion, pale lips, Pale and Thin tongue, Choppy or Fine pulse
Heart-Yin deficiency
Clinical manifestations
Palpitations, insomnia, dream-disturbed sleep, propensity to be startled, poor memory, anxiety, mental restlessness, dry mouth and throat, night sweating, red tongue without coating, Floating-Empty pulse
HT Excess patterns
Heart-Fire blazing
Clinical manifestations
Palpitations, thirst, mouth and tongue ulcers, mental restlessness, feeling agitated, feeling of heat, insomnia, dream-disturbed sleep, red face, dark urine or blood in urine, bitter taste, Red tongue, tip redder and swollen with red points, yellow coating, Full-Rapid-Overflowing pulse
Phlegm-Fire disturbing the Heart
Clinical manifestations
Palpitations, thirst, red face, bitter taste, a feeling of oppression of the chest, expectoration of phlegm, rattling sound in the throat, mental restlessness, insomnia, dream-disturbed sleep, agitation, incoherent speech, mental confusion, rash behavior, tendency to hit or scold people, uncontrolled laughter or crying, shouting, muttering to oneself, mental depression and dullness, manic behavior, Red tongue, redder and swollen tip with red points, yellow dry sticky coating, deep Heart crack, Full-Rapid-Slippery or Rapid-Overflowing- Slippery or Rapid-Full-Wiry pulse
Phlegm misting the Mind
Clinical manifestations
Mental confusion, unconsciousness, incoherent speech, vomiting of phlegm, rattling sound in the throat, mental depression, emotional lability, aphasia, very dull eyes, Swollen tongue with thick-sticky coating, Heart crack, Slippery pulse
Heart-Blood stasis
Clinical manifestations
Palpitations, stabbing or pricking pain in the chest which may radiate to the inner aspect of the left arm or to the shoulder, a feeling of oppression or constriction of the chest, cyanosis of lips and nails, cold hands, tongue Purple in its entirety or only on the sides in the chest area, Choppy, Wiry or Knotted pulse
Small intestine Full patterns
Full-Heat in the Small Intestine
Clinical manifestations
Mental restlessness, insomnia, tongue and/or mouth ulcers, pain in the throat, deafness, uncomfortable feeling and heat sensation in the chest, abdominal pain, thirst with desire to drink cold liquids, scanty and dark urine, burning pain on urination, blood in urine, Red tongue with redder and swollen tip, yellow coating, Overflowing-Rapid pulse especially in the Front position
Small Intestine-Qi pain
Clinical manifestations
Lower abdominal twisting pain which may extend to back, abdominal distension, dislike of pressure on abdomen, borborygmi, flatulence, pain in the testis, white tongue coating. Deep-Wiry pulse, especially on the Rear positions
Infestation of worms in the Small Intestine
Clinical manifestations
Abdominal pain and distension, bad taste in mouth, sallow complexion
Roundworms (ascarid): abdominal pain, vomiting of roundworms, cold limbs
Hookworms: desire to eat strange objects such as soil, wax, uncooked rice or tea leaves
Pinworms: itchy anus, worse in the evening
Tapeworms: constant hunger
Spleen Empty patterns
Spleen-Qi deficiency
Clinical manifestations
Poor appetite, slight abdominal distension after eating, tiredness, lassitude, desire to lie down, pale complexion, weakness of the limbs, loose stools, Pale tongue, Empty pulse
Spleen-Yang deficiency
Clinical manifestations
Poor appetite, slight abdominal distension after eating, tiredness, lassitude, desire to lie down curled up, pale complexion, weakness of the limbs, loose stools, feeling cold, cold limbs, oedema, Pale and wet tongue, Deep-Weak pulse
Spleen-Qi sinking
Clinical manifestations
Poor appetite, slight abdominal distension after eating, tiredness, lassitude, pale complexion, weakness of the limbs, loose stools, depression, tendency to obesity, a bearing-down sensation in the abdomen, prolapse of stomach, uterus, anus or bladder, frequency and urgency of urination, menorrhagia, Pale tongue, Weak pulse
Spleen not controlling Blood
Clinical manifestations
Poor appetite, slight abdominal distension after eating, tiredness, lassitude, pale-sallow complexion, weakness of the limbs, loose stools, depression, blood spots under the skin, blood in the urine or stools, excessive uterine bleeding, Pale tongue, Weak or Fine pulse
Stomach Empty patterns
Stomach-Yin deficiency
Clinical manifestations
No appetite or slight hunger but no desire to eat, constipation (dry stools), dull or slightly burning epigastric pain, dry mouth and throat especially in the afternoon, with desire to drink in small sips, slight feeling of fullness after eating
Tongue: red without coating in the centre, or with rootless coating
Pulse: Floating-Empty on the Right-Middle position
Stomach Full patterns
Stomach-Heat
Clinical manifestations
Burning epigastric pain, intense thirst with desire to drink cold liquids, mental restlessness, bleeding gums, dry stools, dry mouth, mouth ulcers, sour regurgitation, nausea, vomiting soon after eating, excessive hunger, foul breath, a feeling of heat, tongue Red in the centre with a dry yellow or dark yellow(or even black) coating, Rapid and slightly Overflowing pulse on the Right-Middle position
Cold invading the Stomach
Clinical manifestations
Sudden severe pain in the epigastrium, a feeling of cold, cold limbs, preference for warmth, vomiting of clear fluids (which may alleviate the pain), nausea, feeling worse after swallowing cold fluids which are quickly vomited, preference for warm liquids, thick white tongue coating, Deep-Tight-Slow pulse
Retention of Food in the Stomach
Clinical manifestations
Fullness, pain and distension of the epigastrium which are relieved by vomiting, nausea, vomiting of sour fluids, foul breath, sour regurgitation, belching, insomnia, loose stools or constipation, poor appetite Tongue: thick coating (which could be white or yellow) Pulse: Full-Slippery
Lung Empty patterns
Lung-Qi deficiency
Clinical manifestations
Slight shortness of breath, slight cough, weak voice, spontaneous daytime sweating, dislike of speaking, bright pale complexion, propensity to catch colds, tiredness, dislike of cold, Pale tongue, Empty pulse, especially on the Right-Front position
Lung-Yin deficiency
Clinical manifestations
Cough which is dry or with scanty sticky sputum, weak and/hoarse voice, dry mouth and throat, tickly throat, tiredness, dislike of speaking, thin body or thin chest, night sweating, red tongue, dry without coating, Floating-Empty pulse
Lung Dryness
Clinical manifestations
Dry cough, dry skin, dry throat, dry mouth, thirst, hoarse voice, dry tongue, Empty pulse, especially on the Right-Front position
Lung Full patterns
Exterior
• Invasion of Lungs by Wind-Cold
Clinical manifestations
Aversion to cold, fever, cough, itchy throat, slight breathlessness, stuffed or runny nose with clear, watery discharge, sneezing, occipital headache, body aches, thin white tongue coating, Floating-Tight pulse
• Invasion of Lungs by Wind-Heat
Clinical manifestations
Aversion to cold, fever, cough, sore throat, stuffed or runny nose with yellow discharge, headache, body aches, slight sweating, slight thirst, swollen tonsils, tongue slightly Red on the sides in the chest areas or on the front part, Floating-Rapid pulse
• Invasion of Lungs by Wind-Water
Clinical manifestations
Sudden swelling of eyes and face gradually spreading to the whole body, bright shiny complexion, scanty and clear urination, aversion to wind, fever, cough, slight breath lessness, sticky white tongue coating, Floating-Slippery pulse
Interior
• Lung-Heat
Clinical manifestations
Cough, slight breathlessness, feeling of heat, chest ache, flaring of nostrils, thirst, red face, Red tongue with yellow coating, Overflowing-Rapid pulse
• Damp-Phlegm in the Lungs
Clinical manifestations
Chronic cough coming in bouts with profuse sticky white sputum which is easy to expectorate, white pasty complexion, a feeling of oppression in the chest, phlegm in the throat, shortness of breath, dislike of lying down, wheezing, nausea, a feeling of heaviness, muzziness and dizziness of the head, Swollen tongue with a sticky white coating, Slippery or Soggy pulse
• Phlegm-Heat in the Lungs
Clinical manifestations
Barking cough with profuse sticky yellow or green sputum, shortness of breath, wheezing, a feeling of oppression of the chest, phlegm in the throat, a feeling of heat, thirst, insomnia, agitation, a feeling of heaviness and muzziness of the head, dizziness, Red, Swollen tongue with a sticky yellow coating, Slippery-Rapid pulse
Larger Intestine Full patterns
Damp-Heat in the Large Intestine
Clinical manifestations
Abdominal pain that is not relieved by a bowel movement, abdominal fullness, diarrhea, mucus and blood in stools, offensive odour of stools, burning in the anus, scanty dark urine, fever, sweating which does not decrease the fever, a feeling of heat, thirst without desire to drink, feeling of heaviness of the body and limbs, Red tongue with sticky yellow coating, Slippery-Rapid pulse
Heat in the Large Intestine
Clinical manifestations
Constipation with dry stools, burning sensation in the mouth, dry tongue, burning and swelling in anus, scanty dark urine, thick yellow (or brown or black) dry tongue coating, Full-Rapid pulse
Cold invading the Large Intestine
Clinical manifestations
Sudden, cramping abdominal pain, diarrhea with pain, feeling of cold, cold sensation in abdomen, thick white tongue coating, Deep-Tight pulse
Kidney Empty patterns
Kidney-Yang deficiency
Clinical manifestations
Lower backache, cold and weak knees, sensation of cold in the lower back, feeling cold, weak legs, bright-white complexion, tiredness, lassitude, abundant clear urination, urination at night, apathy, oedema of the legs, infertility in women, loose stools, depression, impotence, premature ejaculation, low sperm count, decreased libido, Pale and wet tongue, Deep-Weak pulse
Kidney-Yin deficiency
Clinical manifestations
Dizziness, tinnitus, vertigo, poor memory, hardness of hearing, night sweating, dry mouth and throat at night, lower backache, ache in bones, nocturnal emissions, constipation, dark scanty urine, infertility, premature ejaculation, tiredness, lassitude, depression, slight anxiety, red tongue without coating, Floating-Empty pulse
Kidney-Qi not Firm
Clinical manifestations
Soreness and weakness of the lower back, weak knees, clear frequent urination, weak-stream urination, abundant urination, dribbling after urination, incontinence of urine, enuresis, urination at night, nocturnal emissions without dreams, premature ejaculation, spermatorrhoea, tiredness, feeling cold, cold limbs, in women prolapse of uterus, chronic white vaginal discharge, a dragging-down feeling in the lower abdomen, recurrent miscarriage, Pale tongue, Deep-Weak pulse especially in the Rear positions
Kidney failing to receive Qi
Clinical manifestations
Shortness of breath on exertion, rapid and weak breathing, difficulty in inhaling, chronic cough and/or asthma, spontaneous sweating, cold limbs, cold limbs after sweating, swelling of the face, thin body, mental listlessness, clear urination during asthma attack, lower backache, dizziness, tinnitus, Pale tongue, Deep-Weak-Tight pulse
Kidney-Essence deficiency
Clinical manifestations in children
Poor bone development, late closure of fontanelle, deafness, mental dullness or retardation
Clinical manifestations in adults
Softening of bones, weakness of knees and legs, poor memory, loose teeth, falling hair or premature greying of hair, weakness of sexual activity, lower backache, infertility, sterility, primary amenorrhoea, dizziness, tinnitus, deafness, blurred vision, absent-mindedness, decreased mental sharpness, tongue red without coating if there is Kidney-Yin deficiency; Pale if there is Kidney-Yang deficiency, Floating-Empty or Leather pulse
Empty/Full patterns
Kidney-Yang deficiency, Water over flowing
Kidney-Yin deficiency, Empty-Heat blazing
Combined patterns
Kidney- and Liver-Yin deficiency
Kidneys and Heart not harmonized
Kidney- and Lung-Yin deficiency
Kidney- and Spleen-Yang deficiency
Bladder Full patterns
Damp-Heat in the Bladder
Clinical manifestations
Frequent and urgent urination, burning on urination, difficult urination (stopping in the middle of flow), dark-yellow and/or turbid urine, blood in the urine, fever, thirst with no desire to drink, hypogastric fullness and pain, feeling of heat, thick sticky yellow tongue coating on the root with red spots, pulse Slippery-Rapid and slightly Wiry on the Left-Rear position
Damp-Cold in the Bladder
Clinical manifestations
Frequent and urgent urination, difficult urination (stopping in mid-stream), feeling of heaviness in hypogastrium and urethra, pale and turbid urine, white sticky tongue coating on root, pulse Slippery-Slow and slightly Wiry on Left-Rear position
Greater Yang stage (Tai Yang)
• Invasion of Wind-Cold with prevalence of Wind (Zhong Feng)
• Invasion of Wind-Cold with prevalence of Cold (Shang Han)
Bright Yang stage (Yang Ming)
• Bright Yang channel pattern
• Bright Yang organ pattern
Lesser Yang stage (Shao Yang)
Greater Yin stage (Tai Yin)
Lesser Yin stage (Shao Yin)
• Cold transformation
• Heat transformation
Terminal Yin stage (Jue Yin)
Greater Yang stage (Tai Yang)
Invasion of Wind-Cold with prevalence of Wind (Attack of Wind)
Clinical manifestations
Slight aversion to cold, aversion to wind, slight fever, slight sweating, headache, stiff neck, sneezing, Floating-Slow pulse
Invasion of Wind-Cold with prevalence of Cold (Attack of Cold)
Clinical manifestations
Aversion to cold, slight fever, no sweating, headache, stiff neck, sneezing, runny nose with white discharge, breathlessness, Floating-Tight pulse
Bright Yang stage (Yang Ming)
Bright Yang channel pattern
Clinical manifestations
High fever, profuse sweating, intense thirst, red face, feeling of heat, irritability, delirium, Red tongue with yellow coating, Overflowing-Rapid or Big-Rapid pulse
Bright Yang organ pattern
Clinical manifestations
High fever that is worse in the afternoon, profuse sweating, sweating on limbs, abdominal fullness and pain, constipation, dry stools, thirst, dark urine, Red tongue with thick dry yellow coating, Deep-Full-Slippery-Rapid pulse
Lesser Yang stage (Shao Yang)
Clinical manifestations
Alternation of shivers (or cold feeling) and fever (or feeling of heat), bitter taste, dry throat, blurred vision, hypochondrial fullness and distension, no desire to eat or drink, irritability, nausea, vomiting, unilateral thin white coating, Wiry-Fine pulse
Greater Yin stage (Tai Yin)
Clinical manifestations
Abdominal fullness, feeling cold, vomiting, no appetite, diarrhea, no thirst, tiredness, Pale tongue with sticky white coating, Deep-Weak-Slow pulse
Lesser Yin stage (Shao Yin)
Lesser Yin Cold transformation
Clinical manifestations
Chills, feeling cold, lying with body curled, listlessness, desire to sleep, cold limbs, diarrhea, no thirst, frequent clear urination, Pale and moist Tongue, weaker slow pulse
Lesser Yin Heat transformation
Clinical manifestations
Feeling of heat, irritability, insomnia, dry mouth and throat at night, dark urine, night sweating, Red tongue without coating, Fine-Rapid pulse
Terminal Yin stage (Jue Yin)
Clinical manifestations
Persistent thirst, feeling of energy rising to the chest, pain and heat sensation in heart region, hungry but no desire to eat, cold limbs, diarrhea, vomiting, vomiting of roundworms, Wiry pulse
The Four Levels
Defensive Qi level (Wei)
Qi level (Qi)
Nutritive Qi level (Ying)
Blood level (Xue)
• Invasion of Wind-Cold with prevalence of Wind (Zhong Feng)
• Invasion of Wind-Cold with prevalence of Cold (Shang Han)
Defensive Qi level (Wei)
The Defensive Qi level is the beginning stage of invasions of Wind-Heat: it is the only exterior level
The Defensive Qi level comprises four different patterns according to the nature of the pathogenic factor: Wind-Heat, Summer- Heat, Damp-Heat and Dry-Heat.
Qi level (Qi)
fever, thirst, sweating, feeling of heat, mental restlessness, Red tongue with thick yellow coating and a Rapid-Full pulse.
These are just general symptoms as other manifestations depend on the pattern involved, of which there are five: Lung-Heat (Heat in chest and diaphragm), Stomach-Heat, Intestines Dry-Heat, Gall Bladder-Heat and Damp-Heat in Stomach and Spleen.
Nutritive Qi level (Ying)
At the Nutritive Qi level, the Heat has penetrated to a deeper energetic layer and begun to injure the Yin. At this level, Heat is obstructing the Mind and the Pericardium, causing delirium and even coma. Fever at night is a distinctive sign of the Nutritive Qi level.
The tongue is Deep-Red without coating
Blood level (Xue)
• There is Yin deficiency
• Heat is affecting the Blood, causing bleeding
• Heat is affecting the Mind, causing delirium or coma
• Heat in the Blood causes bleeding under the skin with the appearance of macules
• Internal Wind develops, causing convulsions and tremors
• Collapse of Yin or Yang may occur
-
Meridians and Points
-
Meridians
-
Special Points
Chest | Hand | Face | Foot | |
First circuit |
|
|
|
|
Second circuit |
|
|
|
|
Third circuit |
|
|
|
|
12 regular channels passing route.
12 Regular Channels Distribution | |||
Vertex | LV, UB | Origin | LU: Middle Jiao |
Eye | LV, HT | ST: LI20 | |
Both Canthus | SI | HT: Heart | |
Ear | SI, SJ, GB | KD: Beneath little toe | |
Gums | Upper Gum: ST | PC: Chest | |
Lower Gum: LI | Genital | LV | |
Supraclavicular fossa | All Yang channels except UB | Tail Bone | KD |
Crossing diaphragm | All channels except UB | Sacral Foramen | UB, GB |
Eight Extraordinary Meridians Distribution | |||||||
Yang Qiao & Yin Qiao | Yang Qiao & Yang Wei | Brain | Vertex | Infraorbital region | Lips | Supraclavicular fossa | Throat |
UB1 | SI10 GB20 DU16 | DU Yang Qiao Yin Qiao | DU | Ren | Ren Chong | Yin Qiao | Ren Chong Yin Wei |
The five shu-points
The five shu-points points of the yin channels (and their corresponding phase) | |||||
Jing-Well (Wood) | Ying-Spring (Fire) | Shu-Stream (Earth) | Jing-River (Metal) | He-Sea (Water) | |
Lung | Shaoshang LU-11 | Yuji LU-10 | Taiyuan LU-9 | Jingqu LU-8 | Chize LU-5 |
Spleen | Yinbai SP-1 | Dadu SP-2 | Taibai SP-3 | Shangqiu SP-5 | Yinlingquan SP-9 |
Heart | Shaochong HE-9 | Shaofu HE-8 | Shenmen HE-7 | Lingdao HE-4 | Shaohai HE-3 |
Kidney | Yongquan KID-I | Rangu KID-2 | Taixi KID-3 | Fuliu KID-7 | Yingu KID-1 0 |
Pericardium | Zhongchong P-9 | Laogong P-8 1 | Daling P-7 | Jianshi P-5 | Quze P-3 |
Liver | Dadun LIV-1 | Xingjian LIV-2 | Taichong LIV-3 | Zhongfeng LIV-4 | Ququan LIV-8 |
•jing-well points for fullness below the Heart.
•ying-spring points for heat in the body.
•shu-stream points for heaviness of the body and pain of the joints.
•jing-river points for cough and dyspnoea, chills and fever.
•he-sea points for counterflow qi and diarrhoea.
The five shu-points points of the yang channels (and their corresponding phase) | |||||
Jing-Well (Metal) | Ying-Spring (Water) | Shu-Stream (Wood) | Jing-River (Fire) | He-Sea (Earth) | |
Large Intestine | Shangyang LI-1 | Erjian LI-2 | Sanjian LI-3 | Yangxi LI-5 | Quchi LI-11 |
Stomach | Lidui ST-45 | Neiting ST-44 | Xiangu ST-43 | Jiexi ST-41 | Zusanli ST-36 |
Small Intestine | Shaoze SI-1 | Qiangu SI-2 | Houxi Sl-3 | Yanggu SI-5 | Xiaohai SI-8 |
Bladder | Zhiyin BL-67 | Zutonggu BL-66 | Shugu BL-65 | l<unlun BL-60 | Weizhong BL-40 |
Sanjiao | Guanchong SJ-1 | Yemen SJ-2 | Zhongzhu SJ-3 | Zhigou SJ-6 | Tianjing SJ-10 |
Gall Bladder | Zuqiaoyin GB-44 | Xiaxi GB-43 | Zulinqi GB-41 | Yangfu GB-38 | Yanglingquan GB-34 |
In cases of deficiency reinforce the mother, in cases of excess reduce the child
The mother-child points of the twelve channels | ||
Mother point | Child point | |
Lung | Taiyuan LU-9 | Chize LU-5 |
Large Intestine | Quchi LI-11 | Erjian LI-2 |
Stomach | Jiexi ST-41 | Lidui ST-45 |
Spleen | Dadu SP-2 | Shangqiu SP-5 |
Heart | Shaochong HE-9 | Shenrnen HE-7 |
Small intestine | Houni SI-3 | Xiaohai SI-8 |
Bladder | Zhiyin BL-67 | Shugu BL-65 |
Kidney | Fuliu KID-7 | Yongquan KID-1 |
Pericardium | Zhongchong P-9 | Daling P-7 |
Sanjiao | Zhongzhu SJ-3 | Tianjing SJ-10 |
Call Bladder | Xiaxi GB-43 | Yangfu GB-38 |
Liver | Ququan LIV-8 | Xingjian LIV-2 |
The yuan-source points of the twelve channels | |||
Taiyuan LU-9 | Large Intestine | Hegu LI -4 | |
spleen | Taibai SP-3 | Stomach | Chongyang ST-42 |
Kidney | Taixi KID-3 | Bladder | Jinggu BL-64 |
Heart | Shenrnen HE-7 | Small Intestine | Wangu SI -4 |
Pericardium | Daling P-7 | Sanjiao | Yangchi 51-4 |
Liver | Taichong LIV-3 | Call Bladder | Qiuxu CB-40 |
The luo-connecting points of the twelve channel | |||
Lung | Lieque LU - 7 | Large Intestine | Pianli LI -6 |
spleen | Gongsun SP-4 | Stomach | Fenglong ST -40 |
Kidney | Dazhong KID -4 | Bladder | Feiyang BL-58 |
Heart | Tongli HE-5 | Small Intestine | Zhizheng SI-7 |
Pericardium | Neiguan P -6 | Sanjiao | Waiguan SI -5 |
Liver | Ligou LIV-5 | Gall Bladder | Guangming GB-37 |
THE XI-CLEFT POINTS
The xi-deft points of the twelve channels | |||
Lung | Kongzui LU-6 | Large Intestine | Wenliu LI-7 |
Spleen | Diji SP-8 | Stomach | Liangqiu ST-34 |
Heart Yinxi | HE-6 | Small Intestine | Yanglao SI-6 |
Kidney | Shuiquan KID-5 | Bladder | Jinmen BL-63 |
Pericardium | Ximen P-4 | Sanjiao | Huizong SJ-7 |
Liver | Zhongdu LIV-6 | Gall Bladder | Waiqiu GB-36 |
The xi-deft points of the extraordinary channels | |||
Yang Motility | Fuyang BL-59 | Yang Linking | Yangjiao GB-35 |
Yin Motility | Jiaoxin KID-8 | Yin Linking | Zhubin KID-9 |
The back-shu points of the twelve zangfu | |||||||||||
LU | LI | ST | SP | HT | SI | UB | KD | PC | SJ | GB | LV |
BL13 | UB25 | UB21 | UB20 | UB15 | UB27 | UB28 | UB23 | UB14 | UB22 | UB19 | UB18 |
The front-mu points of the twelve zangfu | |||||||||||
LU | LI | ST | SP | HT | SI | UB | KD | PC | SJ | GB | LV |
LU1 | ST25 | RN12 | LV13 | RN14 | RN4 | RN3 | GB25 | RN17 | RN5 | GB24 | LV14 |
ZANG | FU | QI | BLOOD | SINEWS | VESSEL | BONE | MARROW |
LV13 | RN12 | RN17 | UB17 | GB34 | LU9 | UB11 | GB39 |
THE CONFLUENT POINTS OF THE EIGHT EXTRAORDINARY VESSELS | |||||||
REN | YIN QIAO | DU | YANG QIAO | DAI | YANG WEI | CHONG | YIN WEI |
LU7 | KD6 | SI3 | UB62 | GB41 | SJ5 | SP4 | PC6 |
Lower He-Sea Points | |||||
3 Arm Yang | 3 Leg Yang | ||||
LI | SI | SJ | ST | UB | GB |
ST37 | ST39 | UB39 | ST36 | UB40 | GB34 |
Four Commands Points | 5 Commands | 6 Commands | |||
ST36 | UB40 | LU7 | LI4 | PC6 | DU26 |
Abdomen | Lumbar, back | Head, Nape | Face, Mouth | Chest, Lateral costal | Resuscitation |